Sustained virological response is associated with clearance of hepatitis C virus RNA and a decrease in hepatitis C virus antibody
- PMID: 19076273
- PMCID: PMC2711258
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01918.x
Sustained virological response is associated with clearance of hepatitis C virus RNA and a decrease in hepatitis C virus antibody
Abstract
Background/aim: Viral eradication in chronic hepatitis C patients with sustained virological response (SVR) after interferon (IFN) therapy remains controversial.
Methods: During a long-term follow-up study, 157 patients with SVR to IFN-alpha-2b-based therapy were investigated with a transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) assay in serum. The hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody was assessed by measuring the optical density (OD) (Axsym HCV v3.0) and the semiquantitative titres (RIBA HCV v3.0) of the HCV antibodies directed against the core, NS3, NS4 and NS5 proteins. A control group included 23 untreated patients with persistently normal serum alanine aminotransferase and detectable serum HCV-RNA.
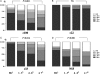
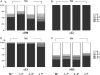
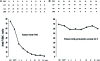
Results: The median duration of follow-up was 4.0 (0-10) years. Serum HCV-RNA remained undetectable in all patients. The mean HCV antibody OD were 93 +/- 19 and 45 +/- 21 before therapy and in the last available serum sample respectively (P=0.001). There was a marked decrease in the HCV antibodies directed against the NS3, NS4 and NS5 proteins (P=0.001), while the core protein titre remained strongly positive. The 23 control patients were followed for a median of 5 (2-14) years. The mean HCV antibody OD were 65 +/- 14 and 64 +/- 19 in the first and the last measurements, respectively (NS), and HCV antibody titres for structural and non-structural proteins remained unchanged.
Conclusion: This long-term study evaluating 157 patients demonstrated that SVR assessed by TMA is durable, and HCV antibodies were markedly decreased (mainly those directed against the non-structural proteins), emphasizing an absence of ongoing infection. These results strongly suggest that HCV infection cured in patients who achieve an SVR.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sustained viral response after interferon-based therapy in chronic hepatitis C: more evidence to support a life-long cure.Liver Int. 2009 Apr;29(4):481-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02000.x. Liver Int. 2009. PMID: 19323778 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Long-term histologic improvement and loss of detectable intrahepatic HCV RNA in patients with chronic hepatitis C and sustained response to interferon-alpha therapy.Ann Intern Med. 1997 Nov 15;127(10):875-81. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-10-199711150-00003. Ann Intern Med. 1997. PMID: 9382365
-
Prevalence of IFNL3 rs4803217 single nucleotide polymorphism and clinical course of chronic hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jun 7;23(21):3815-3824. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3815. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28638221 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody status in patients with chronic hepatitis C after eradication of HCV infection by interferon therapy.Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Mar 15;40(6):e49-54. doi: 10.1086/428128. Epub 2005 Feb 18. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15736006
-
Clinical characteristics of patients with chronic hepatitis C showing biochemical remission, without hepatitis C virus eradication, as a result of interferon therapy. The Osaka Liver Disease Study Group.J Viral Hepat. 2000 Sep;7(5):343-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2000.00250.x. J Viral Hepat. 2000. PMID: 10971822 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerance of interferon-alpha(2b) in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in haemodialysis patients. Pre- and post-renal transplantation assessment.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999 Nov;14(11):2704-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/14.11.2704. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10534516 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Occult hepatitis C virus infection and its relevance in clinical practice.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2011 Dec;1(3):185-9. doi: 10.1016/S0973-6883(11)60130-8. Epub 2012 Jan 2. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 25755384 Free PMC article.
-
Change in hepatitis C virus positivity among needle-stick injury source patients: a 10-year experience in a Japanese tertiary hospital.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Apr 30;21(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06117-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33931015 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Humoral Immune Response towards HCV Genotype 4 Using a Bead-Based Multiplex Serological Assay.High Throughput. 2017 Oct 30;6(4):15. doi: 10.3390/ht6040015. High Throughput. 2017. PMID: 29855459 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C: viral and host factors associated with non-response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin.Liver Int. 2010 Oct;30(9):1259-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02283.x. Liver Int. 2010. PMID: 20633102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Favorable Outcomes of Chinese HCV-Related Cirrhotic Patients with Sustained Virological Response after Pegylated Interferon Plus Ribavirin Treatment.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:8061091. doi: 10.1155/2017/8061091. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28232944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcellin P, Boyer N, Gervais A, et al. Long-term histologic improvement and loss of detectable intrahepatic HCV RNA in patients with chronic hepatitis C and sustained response to interferon-alpha therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:875–81. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–65. - PubMed
-
- Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H, Jr, Morgan TR, et al. Peginterferon-a2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346–55. - PubMed
-
- McHutchison JG, Poynard T, Esteban-Mur R, et al. Hepatic HCV RNA before and after treatment with interferon alone or combined with ribavirin. Hepatology. 2002;35:688–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

