Mitochondrial and nuclear cross talk in cell death: parthanatos
- PMID: 19076445
- PMCID: PMC4454457
- DOI: 10.1196/annals.1427.014
Mitochondrial and nuclear cross talk in cell death: parthanatos
Abstract
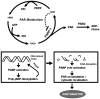
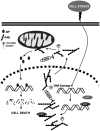
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is an abundant nuclear protein best known to facilitate DNA base excision repair. Recent work has expanded the physiologic functions of PARP-1, and it is clear that the full range of biologic actions of this important protein are not yet fully understood. Regulation of the product of PARP-1, poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR), is a dynamic process with PAR glycohydrolase playing the major role in the degradation of the polymer. Under pathophysiologic situations overactivation of PARP-1 results in unregulated PAR synthesis and widespread neuronal cell death. Once thought to be necrotic cell death resulting from energy failure, we have found that PARP-1-dependent cell death is dependent on the generation of PAR, which triggers the nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor resulting in caspase-independent cell death. This form of cell death is distinct from apoptosis, necrosis, or autophagy and is termed parthanatos. PARP-1-dependent cell death has been implicated in tissues throughout the body and in diseases afflicting hundreds of millions worldwide, including stroke, Parkinson's disease, heart attack, diabetes, and ischemia reperfusion injury in numerous tissues. The breadth of indications for PARP-1 injury make parthanatos a clinically important form of cell death to understand and control.
Figures
References
-
- Smith S. The world according to PARP. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:174–9. - PubMed
-
- Hong SJ, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:259–64. - PubMed
-
- Ame JC, Spenlehauer C, de Murcia G. The PARP superfamily. Bioessays. 2004;26:882–93. - PubMed
-
- Virag L, Szabo C. The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:375–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

