Extinction of morphine-dependent conditioned behavior is associated with increased phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors at hippocampal synapses
- PMID: 19077125
- PMCID: PMC2662612
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06560.x
Extinction of morphine-dependent conditioned behavior is associated with increased phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors at hippocampal synapses
Abstract
In abstinent opiate addicts, relapse can be triggered by exposure to environmental cues associated with drug use; thus, the disruption of these learned associations may be an effective approach for reducing relapse. Interestingly, glutamatergic systems are thought to be involved in opiate-induced behavioral plasticity. In this study, changes in expression and phosphorylation levels of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) glutamate receptor subunits (GluR1, GluR2) in the hippocampus were investigated in rats showing a conditioned response (CR) to an opiate-paired environment as well as in animals in which this conditioned behavior was extinguished. Additionally, another set of animals went through a drug-unpaired paradigm (without conditioning) in order to examine the effects of the pharmacology of the drug itself. Subcellular fractionation techniques were used to analyse the local distribution of AMPA glutamate subunits within the synapse, especially at the postsynaptic density (PSD). Results showed that morphine-dependent CRs did not alter expression or redistribution of GluR1 or GluR2; however, the unpaired administration of morphine resulted in an increase in the phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit at extrasynaptic sites. Interestingly, the extinction of the CR significantly increased phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit at the PSD. Therefore we propose that, within the synapse, the phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit at the PSD may be a key mechanism in the extinction of opiate-associated CRs.
Figures



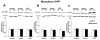
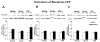

Similar articles
-
Increased insertion of glutamate receptor 2-lacking alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors at hippocampal synapses upon repeated morphine administration.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 May;77(5):874-83. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060301. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20159947 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of opiate-related signaling molecules in morphine-dependent conditioned behavior: conditioned place preference to morphine induces CREB phosphorylation.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Mar;35(4):955-66. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.199. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19956087 Free PMC article.
-
Increased AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit incorporation in rat hippocampal CA1 synapses during benzodiazepine withdrawal.J Comp Neurol. 2008 Dec 20;511(6):832-46. doi: 10.1002/cne.21866. J Comp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18924138 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal GluA1-containing AMPA receptors mediate context-dependent sensitization to morphine.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 9;31(45):16279-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3835-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22072679 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine induces AMPA receptor internalization in primary hippocampal neurons via calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation of GluR1 subunits.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 10;30(45):15304-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4255-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21068335 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Allosteric signaling through an mGlu2 and 5-HT2A heteromeric receptor complex and its potential contribution to schizophrenia.Sci Signal. 2016 Jan 12;9(410):ra5. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aab0467. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 26758213 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of inflammatory pain on CB1 receptor in the midbrain periaqueductal gray.Pain Rep. 2021 Mar 5;6(1):e897. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000897. eCollection 2021 Jan-Feb. Pain Rep. 2021. PMID: 33693301 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptor 1 phosphorylation at serine 831 and 845 modulates seizure susceptibility and hippocampal hyperexcitability after early life seizures.J Neurosci. 2012 Dec 5;32(49):17800-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6121-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23223299 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine-induced apoptosis in the ventral tegmental area and hippocampus after the development but not extinction of reward-related behaviors in rats.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Mar;34(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s10571-013-0007-8. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24281942 Free PMC article.
-
Increased insertion of glutamate receptor 2-lacking alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors at hippocampal synapses upon repeated morphine administration.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 May;77(5):874-83. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060301. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20159947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardo MT, Rowlett JK, Harris MJ. Conditioned place preference using opiate and stimulant drugs: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1995;19:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Biala G, Budzynska B. Reinstatement of nicotine-conditioned place preference by drug priming: effects of calcium channel antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;537:85–93. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context and ambiguity in the extinction of emotional learning: implications for exposure therapy. Behav Res Ther. 1988;26:137–149. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. A learning theory perspective on lapse, relapse, and the maintenance of behavior change. Health Psychol. 2000;19:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52:976–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

