Survivable stereotaxic surgery in rodents
- PMID: 19078946
- PMCID: PMC3233859
- DOI: 10.3791/880
Survivable stereotaxic surgery in rodents
Abstract
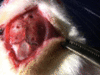
The ability to measure extracellular basal levels of neurotransmitters in the brain of awake animals allows for the determination of effects of different systemic challenges (pharmacological or physiological) to the CNS. For example, one can directly measure how the animal's midbrain dopamine projections respond to dopamine-releasing drugs like d-amphetamine or natural stimuli like food. In this video, we show you how to implant guide cannulas targeting specific sites in the rat brain, how to insert and implant a microdialysis probe and how to use high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrochemical detection (HPLC-EC) to measure extracellular levels of oxidizable neurotransmitters and metabolites. Local precise introduction of drugs through the microdialysis probe allows for refined work on site specificity in a compound s mechanism of action. This technique has excellent anatomical and chemical resolution but only modest time resolution as microdialysis samples are usually processed every 20-30 minutes to ensure detectable neurotransmitter levels. Complementary ex vivo tools (i.e., slice and cell culture electrophysiology) can assist with monitoring real-time neurotransmission.
References
-
- Chen KC. Effects of tissue trauma on the characteristics of microdialysis zero-net-flux method sampling neurotransmitters. Journal of Theor. Biology. 2006;238:863–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources