Enhancing SIV-specific immunity in vivo by PD-1 blockade
- PMID: 19078956
- PMCID: PMC2753387
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07662
Enhancing SIV-specific immunity in vivo by PD-1 blockade
Abstract
Chronic immunodeficiency virus infections are characterized by dysfunctional cellular and humoral antiviral immune responses. As such, immune modulatory therapies that enhance and/or restore the function of virus-specific immunity may protect from disease progression. Here we investigate the safety and immune restoration potential of blockade of the co-inhibitory receptor programmed death 1 (PD-1) during chronic simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection in macaques. We demonstrate that PD-1 blockade using an antibody to PD-1 is well tolerated and results in rapid expansion of virus-specific CD8 T cells with improved functional quality. This enhanced T-cell immunity was seen in the blood and also in the gut, a major reservoir of SIV infection. PD-1 blockade also resulted in proliferation of memory B cells and increases in SIV envelope-specific antibody. These improved immune responses were associated with significant reductions in plasma viral load and also prolonged the survival of SIV-infected macaques. Blockade was effective during the early (week 10) as well as late ( approximately week 90) phases of chronic infection even under conditions of severe lymphopenia. These results demonstrate enhancement of both cellular and humoral immune responses during a pathogenic immunodeficiency virus infection by blocking a single inhibitory pathway and identify a novel therapeutic approach for control of human immunodeficiency virus infections.
Figures
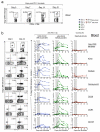
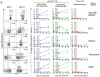
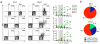
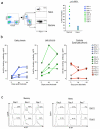
Comment in
-
'Exhaustive' look at PD-1/PDL-1 blockade in vivo.Immunotherapy. 2009 Jul;1(4):525-7. doi: 10.2217/imt.09.37. Immunotherapy. 2009. PMID: 20635984 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wherry EJ, et al. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity. 2007;27:670–684. - PubMed
-
- Klenerman P, Hill A. T cells and viral persistence: lessons from diverse infections. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:873–879. - PubMed
-
- Letvin NL, Walker BD. Immunopathogenesis and immunotherapy in AIDS virus infections. Nat Med. 2003;9:861–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

