Endochondral ossification is required for haematopoietic stem-cell niche formation
- PMID: 19078959
- PMCID: PMC2648141
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07547
Endochondral ossification is required for haematopoietic stem-cell niche formation
Abstract
Little is known about the formation of niches, local micro-environments required for stem-cell maintenance. Here we develop an in vivo assay for adult haematopoietic stem-cell (HSC) niche formation. With this assay, we identified a population of progenitor cells with surface markers CD45(-)Tie2(-)alpha(V)(+)CD105(+)Thy1.1(-) (CD105(+)Thy1(-)) that, when sorted from 15.5 days post-coitum fetal bones and transplanted under the adult mouse kidney capsule, could recruit host-derived blood vessels, produce donor-derived ectopic bones through a cartilage intermediate and generate a marrow cavity populated by host-derived long-term reconstituting HSC (LT-HSC). In contrast, CD45(-)Tie2(-)alpha(V)(+)CD105(+)Thy1(+) (CD105(+)Thy1(+)) fetal bone progenitors form bone that does not contain a marrow cavity. Suppressing expression of factors involved in endochondral ossification, such as osterix and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), inhibited niche generation. CD105(+)Thy1(-) progenitor populations derived from regions of the fetal mandible or calvaria that do not undergo endochondral ossification formed only bone without marrow in our assay. Collectively, our data implicate endochondral ossification, bone formation that proceeds through a cartilage intermediate, as a requirement for adult HSC niche formation.
Figures
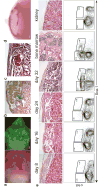
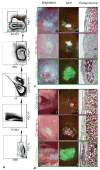
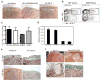
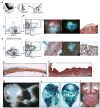
References
-
- Moore KA, Lemischka IR. Stem cells and their niches. Science (New York, N Y. 2006;311(5769):1880–1885. - PubMed
-
- Adams GB, Scadden DT. The hematopoietic stem cell in its place. Nature immunology. 2006;7(4):333–337. - PubMed
-
- Wilson A, Trumpp A. Bone-marrow haematopoietic-stem-cell niches. Nature reviews. 2006;6(2):93–106. - PubMed
-
- Weissman IL. Normal and neoplastic stem cells. Novartis Foundation symposium. 2005;265:35–50. discussion 50-34, 92-37. - PubMed
-
- Kiel MJ, et al. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell. 2005;121(7):1109–1121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

