Cytokines mediating the induction of chronic colitis and colitis-associated fibrosis
- PMID: 19079223
- PMCID: PMC3673699
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2008.41
Cytokines mediating the induction of chronic colitis and colitis-associated fibrosis
Abstract
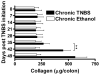
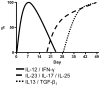
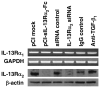
To investigate the immunopathogenesis of inflammation-associated fibrosis we analyzed the chronic colitis and late-developing fibrosis occurring in BALB/c mice administered weekly doses of intrarectal trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). We showed first in this model that an initial T helper type 1 response involving interleukin (IL)-12p70 and interferon-gamma subsides after 3 weeks to be supplanted by an IL-23/IL-25 response beginning after 4-5 weeks. This evolution is followed by gradually increasing production of IL-17 and cytokines ordinarily seen in a T helper type 2 response, particularly IL-13, which reaches a plateau at 8-9 weeks. We then show that IL-13 production results in the induction of an IL-13 receptor formerly thought to function only as a decoy receptor, IL-13Ralpha(2), and this receptor is critical to the production of tumor growth factor (TGF)-beta(1) and the onset of fibrosis. Thus, if IL-13 signaling through this receptor is blocked by administration of soluble IL-13Ralpha(2)-Fc, or by administration of IL-13Ralpha(2)-specific siRNA, TGF-beta(1) is not produced and fibrosis does not occur. These studies show that in chronic TNBS colitis, fibrosis is dependent on the development of an IL-13 response that acts through a novel cell-surface-expressed IL-13 receptor to induce TGF-beta(1).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors claim no financial interest.
Figures
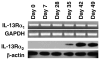

Similar articles
-
Induction of IL-13 triggers TGF-beta1-dependent tissue fibrosis in chronic 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis.J Immunol. 2007 May 1;178(9):5859-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.9.5859. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17442970
-
IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis.Nat Med. 2006 Jan;12(1):99-106. doi: 10.1038/nm1332. Epub 2005 Dec 4. Nat Med. 2006. PMID: 16327802
-
IL-13 signaling via IL-13R alpha2 induces major downstream fibrogenic factors mediating fibrosis in chronic TNBS colitis.Gastroenterology. 2008 Dec;135(6):2003-13, 2013.e1-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.055. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18938165
-
Cytokines in colitis associated cancer: potential drug targets?Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008 Sep;7(3):187-94. doi: 10.2174/187152808785748137. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18782026 Review.
-
The signaling function of the IL-13Ralpha2 receptor in the development of gastrointestinal fibrosis and cancer surveillance.Curr Mol Med. 2009 Aug;9(6):740-50. doi: 10.2174/156652409788970652. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19689301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proton pump inhibitor induced collagen expression in colonocytes is associated with collagenous colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 7;23(9):1586-1593. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1586. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28321159 Free PMC article.
-
Ulcerative colitis: immune function, tissue fibrosis and current therapeutic considerations.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012 Jan;397(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00423-011-0789-4. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012. PMID: 21479621 Review.
-
Baicalin alleviates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway activation.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jul;20(1):581-590. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8718. Epub 2020 May 6. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32537016 Free PMC article.
-
Novel PPARγ Modulator GED-0507-34 Levo Ameliorates Inflammation-driven Intestinal Fibrosis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016 Feb;22(2):279-92. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000618. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016. PMID: 26535766 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of epithelium integrity by inflammation-associated fibroblasts through prostaglandin signaling.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 5;10(14):eadj7666. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj7666. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38569041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck PL, Podolsky DK. Growth factors in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1999;5:44–60. - PubMed
-
- Bouma G, Strober W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature reviews. 2003;3:521–533. - PubMed
-
- Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:182–205. - PubMed
-
- Harper PH, V, Fazio W, Lavery IC, Jagelman DG, Weakley FL, Farmer RG, Easley KA. The long-term outcome in Crohn’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987;30:174–179. - PubMed
-
- Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2002;347:417–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

