CEACAM1 and the regulation of mucosal inflammation
- PMID: 19079227
- PMCID: PMC3901578
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2008.50
CEACAM1 and the regulation of mucosal inflammation
Abstract
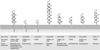
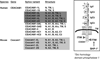
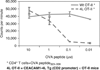
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by unrestrained T-cell activation that results in the production of a variety of inflammatory cytokines and other mediators. Understanding the mechanisms of T-cell regulation is therefore of significant importance to IBD and other forms of dysregulated-mucosal inflammation. An area that is of significant interest are the cell autonomous mechanisms of T-cell regulation through proteins that have natural inhibitory functions when expressed on T lymphocytes. One such molecule is carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1). CEACAM1 is primarily an activation-induced cell-surface molecule that functions as a co-inhibitory receptor. Homophilic ligation of CEACAM1 on T cells leads to a signaling mechanism, which results in inhibition of a broad range T-cell functions. CEACAM1 therefore represents a new potential therapeutic target in the treatment of IBD.
Figures
References
-
- Strober W, Fuss IJ, Blumberg RS. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:495–549. - PubMed
-
- Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007;448:427–434. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 in control of the regulatory T cell lineage. Nat. Immunol. 2007;8:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Mucida D, et al. Reciprocal TH17 and regulatory T cell differentiation mediated by retinoic acid. Science. 2007;317:256–260. - PubMed
-
- Collison LW, et al. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature. 2007;450:566–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

