Messenger RNA targeting to endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling sites
- PMID: 19079237
- PMCID: PMC2768538
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07641
Messenger RNA targeting to endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling sites
Abstract
Deficiencies in the protein-folding capacity of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in all eukaryotic cells lead to ER stress and trigger the unfolded protein response (UPR). ER stress is sensed by Ire1, a transmembrane kinase/endoribonuclease, which initiates the non-conventional splicing of the messenger RNA encoding a key transcription activator, Hac1 in yeast or XBP1 in metazoans. In the absence of ER stress, ribosomes are stalled on unspliced HAC1 mRNA. The translational control is imposed by a base-pairing interaction between the HAC1 intron and the HAC1 5' untranslated region. After excision of the intron, transfer RNA ligase joins the severed exons, lifting the translational block and allowing synthesis of Hac1 from the spliced HAC1 mRNA to ensue. Hac1 in turn drives the UPR gene expression program comprising 7-8% of the yeast genome to counteract ER stress. Here we show that, on activation, Ire1 molecules cluster in the ER membrane into discrete foci of higher-order oligomers, to which unspliced HAC1 mRNA is recruited by means of a conserved bipartite targeting element contained in the 3' untranslated region. Disruption of either Ire1 clustering or HAC1 mRNA recruitment impairs UPR signalling. The HAC1 3' untranslated region element is sufficient to target other mRNAs to Ire1 foci, as long as their translation is repressed. Translational repression afforded by the intron fulfils this requirement for HAC1 mRNA. Recruitment of mRNA to signalling centres provides a new paradigm for the control of eukaryotic gene expression.
Figures

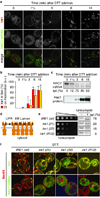

Comment in
-
Cell biology: How to combat stress.Nature. 2009 Feb 5;457(7230):668-9. doi: 10.1038/457668a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19194438 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;22:487–508. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:519–529. - PubMed
-
- van Anken E, Braakman I. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the making of a professional secretory cell. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005;40:269–283. - PubMed
-
- Rüegsegger U, Leber JH, Walter P. Block of HAC1 mRNA translation by long-range base pairing is released by cytoplasmic splicing upon induction of the unfolded protein response. Cell. 2001;107:103–114. - PubMed
-
- Sidrauski C, Cox JS, Walter P. tRNA ligase is required for regulated mRNA splicing in the unfolded protein response. Cell. 1996;87:405–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

