Inhibition of tubulointerstitial fibrosis by pentoxifylline is associated with improvement of vascular endothelial growth factor expression
- PMID: 19079293
- PMCID: PMC4006533
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2008.11
Inhibition of tubulointerstitial fibrosis by pentoxifylline is associated with improvement of vascular endothelial growth factor expression
Abstract
Aim: Recent information indicates that pentoxifylline (PTX) has the ability to suppress inflammation and profibrotic cell proliferation. In this study, we investigated the effect of PTX on tubulointerstitial fibrosis and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in a rat model of obstructive nephropathy.
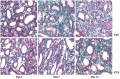
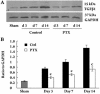
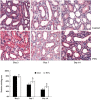
Methods: Wistar rats with left ureteral ligation were divided into control and PTX-treated groups. The histopathologic degree of tubulointerstitial fibrosis was scored with PAS and Masson-stained sections. The protein and mRNA for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were semiquantitatively measured with immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR. The protein for transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) and hypoxia-induced factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) was determined by Western blot.
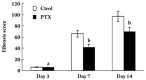
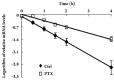
Results: Compared with the control group, PTX treatment reduced fibrosis scores at d 7 and d 14 (P<0.05). The reduction was accompanied by inhibited expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGFbeta1), a key cytokine in tubulointerstitial fibrogenesis (P<0.01). Meanwhile, VEGF protein and mRNA in the kidney were increased in the PTX-treated group compared with the control group (P<0.01). PTX up-regulated expression of VEGF mRNA in a dose- and time-dependent manner in cultured HK-2 cells (P<0.01). However, expression of HIF-1alpha (a key transcription factor for VEGF gene expression) was unchanged by PTX treatment. PTX prolonged the half-life of VEGF mRNA by a 1.07-fold increase.
Conclusions: PTX inhibited tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a rat model of obstructive nephropathy while preventing loss of VEGF. PTX up-regulated expression of VEGF mRNA through stabilization of its mRNA in cultured renal tubular epithelial cells.
Figures



References
-
- Damico G, Ferrario F, Rastaldi MP. Tubulointerstitial damage in glomerular disease: its role in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;26:124–32. - PubMed
-
- Kang DH, Kanellis J, Hugo C, Truong L, Anderson S, Kerjaschki D, et al. Role of the microvascular endothelium in progressive renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:806–16. - PubMed
-
- Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: A final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Choi YJ, Chakraborty S, Nguyen V, Nguyen C, Kim BK, Shim SI, et al. Peritubular capillary loss is associated with chronic tubulointerstitial injury in human kidney: Altered expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1491–7. - PubMed
-
- Ohashi R, Kitamura H, Yamanaka N. Peritubular capillary injury during the progression of experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11:47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

