Guanylate-binding protein-1 is expressed at tight junctions of intestinal epithelial cells in response to interferon-gamma and regulates barrier function through effects on apoptosis
- PMID: 19079332
- PMCID: PMC2877263
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2008.62
Guanylate-binding protein-1 is expressed at tight junctions of intestinal epithelial cells in response to interferon-gamma and regulates barrier function through effects on apoptosis
Abstract
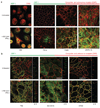
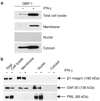
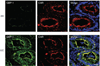
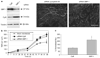
Guanylate-binding protein-1 (GBP-1) is an interferon inducible large GTPase involved in endothelial cell proliferation and invasion. In this report, expression and function of GBP-1 were investigated in vitro in intestinal epithelia after exposure to interferon-gamma and in human colonic mucosa from individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Interestingly, in contrast to other epithelia, GBP-1 distributed to the plasma membrane in intestinal epithelial cells where it colocalized with the tight junction protein coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor. In addition, expression of GBP-1 was upregulated in colonic epithelia of individuals with IBD. Downregulation of GBP-1 by siRNA resulted in enhanced permeability that correlated with increased apoptosis. Indeed, inhibition of caspase activity prevented the inhibition of barrier formation induced by the loss of GBP-1. These data suggest that GBP-1 is a novel marker of intestinal mucosal inflammation that may protect against epithelial apoptosis induced by inflammatory cytokines and subsequent loss of barrier function.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng YS, Colonno RJ, Yin FH. Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate-binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1983;258:7746–7750. - PubMed
-
- Naschberger E, Bauer M, Sturzl M. Human guanylate-binding protein-1 (hGBP-1) characterizes and establishes a nonangiogenic endothelial cell activation phenotype in inflammatory diseases. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2005;45:215–227. - PubMed
-
- Olszewski MA, Gray J, Vestal DJ. In silico genomic analysis of the human and murine guanylate-binding protein (GBP) gene clusters. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006;26:328–352. - PubMed
-
- Prakash B, Praefcke GJ, Renault L, Wittinghofer A, Herrmann C. Structure of human guanylate-binding protein-1 representing a unique class of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 2000;403:567–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

