The laboratory opossum (Monodelphis domestica) as a natural mammalian model for human cancer research
- PMID: 19079623
- PMCID: PMC2600460
The laboratory opossum (Monodelphis domestica) as a natural mammalian model for human cancer research
Abstract
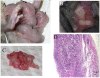
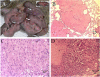
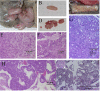
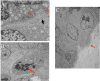
This study established that human cancer cells (A375 melanoma, HT-29 colon cancer, PC-3p prostate cancer) that were xenografted into suckling opossums could proliferate and globally metastasize as early as 11 days after injection. Light and electron microscopic examinations (HT-29 colon cancer) determined that the cellular features exhibited by the xenogeneic human tumors grown in laboratory opossums were consistent with those observed in tumors removed from humans. The tumor induction rate, patterns of tumor growth and regression, and types of host immune responses against the xenografted tumors were influenced by injection dosages, injection sites and injection ages of suckling opossums. The results highlight the value of the opossum model as a natural in vivo system for investigating human cancer growth, metastasis and apoptosis at the cellular and molecular levels; enhancing identification of tumor associated antigens or T cell epitopes through use of humoral and cellular expression cloning techniques; elucidating mechanisms utilized by tumor cells to evade host immunosurveillance; and devising diagnostic and therapeutic methods for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Monodelphis domestica; Opossum; animal model; human cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Aramant R, Turner JE. Cross-species grafting of embryonic mouse and grafting of older postnatal rat retinas into the lesioned adult rat eye: the importance of cyclosporin A for survival. Brain Res. 1988;469:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ. Rationale and methods for the use of nude mice to study the biology and therapy of human cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1986;5:29–49. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS. What is the optimal rodent model for anti-tumor drug testing? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998-1999;17:301–304. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
