Residual cancer burden in locally advanced breast cancer: a superior tool
- PMID: 19079627
- PMCID: PMC2601022
- DOI: 10.3747/co.v15i6.242
Residual cancer burden in locally advanced breast cancer: a superior tool
Abstract
Objectives: Locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) poses a difficult clinical challenge with an overall poor long-term prognosis. The strength of the association between tumour characteristics, treatment response, and outcome is not well defined. In the present study, we attempted to gain further insight into LABC by reviewing tumour characteristics of patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and by studying the association of those characteristics with outcome. We calculated the residual cancer burden (RCB) score obtained at surgery and attempted to study its correlation with event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS).
Methods: We studied patients diagnosed primarily with LABC (n = 45). Pathologic and clinical responses were determined. Pathology slides were reviewed.
Results: Of the 45 study patients, 9% had stage IIB disease; 29%, stage IIIA; 51%, stage IIIB; and 11%, stage IIIC. Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) was found in 16%. Pathologic complete response (pCR) was achieved in 22% of all patients. None of the patients with ibc achieved pcr. Patients with estrogen receptor-negative (ER-)/progesterone receptor-negative (PR-) tumours were more likely to achieve pcr than were those with ER+/PR+ tumours. Among patients with tumours that overexpressed human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu), 17% achieved pCR as compared with 25% of patients with non-overexpressing tumours; only 1 patient had received trastuzumab. The RCB scores were calculated in 32 patients and ranged between 0 and 4.6.
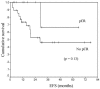
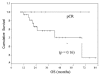
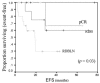
Conclusions: The present study examined practical issues related to the classification and management of LABC and IBC. The RCB, defined from routine pathology materials, was easily quantifiable. It appears to be a better predictor than pCR of outcome following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in LABC. Higher RCB scores were associated with lower efs and a lower rate of os. A continual quest for reliable predictive and correlative prognostic markers, and for better surrogate endpoints for outcome, is essential to advance our understanding of LABC and to improve treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Breast cancer; endpoints; locally advanced disease; pathology; residual disease.
Figures
References
-
- Low JA, Berman AW, Steinberg SM, Danforth DN, Lippman ME, Swain SM. Long-term follow-up for locally advanced and inflammatory breast cancer patients treated with multimodality therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4067–74. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, Ames FC, Buzdar AU, et al. Management of stage iii primary breast cancer with primary chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. Cancer. 1988;62:2507–16. - PubMed
-
- Guarneri V, Broglio K, Kau SW, et al. Prognostic value of pathologic complete response after primary chemotherapy in relation to hormone receptor status and other factors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1037–44. - PubMed
-
- Kuerer HM, Newman LA, Smith TL, et al. Clinical course of breast cancer patients with complete pathologic primary tumor and axillary lymph node response to doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:460–9. - PubMed
-
- Stewart JF, King RJ, Winter PJ, Tong D, Hayward JL, Rubens RD. Oestrogen receptors, clinical features and prognosis in stage iii breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1982;18:1315–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

