Emerging urinary biomarkers in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 19079800
- PMCID: PMC2600533
- DOI: 10.1517/17530059.2.4.387
Emerging urinary biomarkers in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Acute kidney injury (AKI) represents a common and devastating problem in clinical medicine. The lack of early biomarkers for AKI has led to a delay in initiating potentially effective therapies. OBJECTIVE: Identification of novel urinary biomarkers for AKI that have progressed to the clinical phase of the biomarker discovery process. METHODS: A literature review (PubMed, MedLine) from 2000 to the present. RESULTS/CONCLUSIONS;: The most promising AKI biomarkers include neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, IL-18, kidney injury molecule-1 and liver-type fatty acid binding protein. Studies to validate the sensitivity and specificity of these biomarkers in clinical samples from large cohorts and from multiple clinical situations are in progress, facilitated by the development of commercial tools for their measurement.
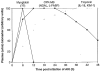
Figures
References
-
- Bagga A, Bakkaloglu A, Devarajan P, et al. Improving outcomes from acute kidney injury: report of an initiative. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:1655–8165. - PubMed
-
- Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R. Acute renal failure. Lancet. 2005;365:417–30. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–8. - PubMed
-
- Palevsky PM. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: the tip of the iceberg. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:6–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
