UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators
- PMID: 19081072
- PMCID: PMC2923556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.015
UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators
Abstract
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is linked to metabolic dysfunction, yet it is not known how endoplasmic reticulum (ER) disruption might influence metabolic pathways. Using a multilayered genetic approach, we find that mice with genetic ablations of either ER stress-sensing pathways (ATF6alpha, eIF2alpha, IRE1alpha) or of ER quality control (p58(IPK)) share a common dysregulated response to ER stress that includes the development of hepatic microvesicular steatosis. Rescue of ER protein processing capacity by the combined action of UPR pathways during stress prevents the suppression of a subset of metabolic transcription factors that regulate lipid homeostasis. This suppression occurs in part by unresolved ER stress perpetuating expression of the transcriptional repressor CHOP. As a consequence, metabolic gene expression networks are directly responsive to ER homeostasis. These results reveal an unanticipated direct link between ER homeostasis and the transcriptional regulation of metabolism, and suggest mechanisms by which ER stress might underlie fatty liver disease.
Figures
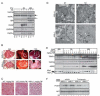
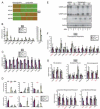

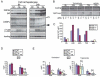



Comment in
-
ER stress and lipogenesis: a slippery slope toward hepatic steatosis.Dev Cell. 2008 Dec;15(6):795-6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.11.013. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 19081067
References
-
- Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A, Mori K. ATF6 Is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct Funct. 2008;33:75–89. - PubMed
-
- Ferre P, Foufelle F. SREBP-1c transcription factor and lipid homeostasis: clinical perspective. Horm Res. 2007;68:72–82. - PubMed
-
- Flodby P, Barlow C, Kylefjord H, Ahrlund-Richter L, Xanthopoulos KG. Increased hepatic cell proliferation and lung abnormalities in mice deficient in CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24753–24760. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Jungries R, Chung P, Plesken H, Sabatini DD, Ron D. Diabetes mellitus and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in perk−/− mice reveals a role for translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol Cell. 2001;7:1153–1163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

