Regulation of Apoptosis by Gram-Positive Bacteria: Mechanistic Diversity and Consequences for Immunity
- PMID: 19081777
- PMCID: PMC2600511
- DOI: 10.2174/157339506776843033
Regulation of Apoptosis by Gram-Positive Bacteria: Mechanistic Diversity and Consequences for Immunity
Abstract
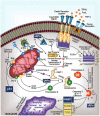
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is an important physiological mechanism, through which the human immune system regulates homeostasis and responds to diverse forms of cellular damage. PCD may also be involved in immune counteraction to microbial infection. Over the past decade, the amount of research on bacteria-induced PCD has grown tremendously, and the implications of this mechanism on immunity are being elucidated. Some pathogenic bacteria actively trigger the suicide response in critical lineages of leukocytes that orchestrate both the innate and adaptive immune responses; other bacteria proactively prevent PCD to benefit their own survival and persistence. Currently, the microbial virulence factors, which represent the keys to unlocking the suicide response in host cells, are a primary focus of this field. In this review, we discuss these bacterial "apoptosis regulatory molecules" and the apoptotic events they either trigger or prevent, the host target cells of this regulatory activity, and the possible ramifications for immunity to infection. Gram-positive pathogens including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Listeria, and Clostridia species are discussed as important agents of human infection that modulate PCD pathways in eukaryotic cells.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Y, Zychlinsky A. Apoptosis induced by bacterial pathogens. Microb Pathog. 1994;17(4):203–12. - PubMed
-
- Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A. The induction of apoptosis by bacterial pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53:155–87. - PubMed
-
- Behnia M, Robertson KA, Martin WJ., 2nd Lung infections: role of apoptosis in host defense and pathogenesis of disease. Chest. 2000;117(6):1771–7. - PubMed
-
- Navarre WW, Zychlinsky A. Pathogen-induced apoptosis of macrophages: a common end for different pathogenic strategies. Cell Microbiol. 2000;2(4):265–73. - PubMed
-
- Dockrell DH. Apoptotic cell death in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. J Infect. 2001;42(4):227–34. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
