Three generic nevirapine-based antiretroviral treatments in Chinese HIV/AIDS patients: multicentric observation cohort
- PMID: 19081791
- PMCID: PMC2597744
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003918
Three generic nevirapine-based antiretroviral treatments in Chinese HIV/AIDS patients: multicentric observation cohort
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of three nevirapine-based antiretroviral treatments for adult antiretroviral-naïve Chinese patients with HIV-1 infection.
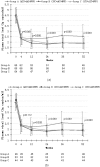
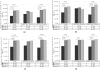
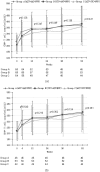
Methodology: This was a prospective, multicenter study. 198 antiretroviral-naïve HIV-1 positive subjects with CD4 lymphocyte counts between 100/ul and 350/ul and plasma HIV-1 RNA levels more than 500 copies/ml were randomized to start three NVP-based antiretroviral treatments: group A, NVP+AZT+ddI; group B, NVP+3TC+d4T; group C, NVP+AZT+3TC. Viral responses, immunologic responses, adverse events and drug resistance were monitored at baseline and the end of week 4, 12, 24, 36, 52. Viralogical response and immunological response were also compared in different strata of baseline CD4 T lymphocyte counts and plasma HIV-1 RNA concentrations. At baseline, the plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.44+/-0.68, 4.52+/-0.71 and 4.41+/-0.63 lg copies/ml in group A, B and C respectively (p = 0.628). At the end of the study, the plasma viral load reached 2.54+/-1.11, 1.89+/-0.46 and 1.92+/-0.58 lg copies/ml in group A, B and C respectively (p<0.001). At week 52, suppression of plasma HIV-1 RNA to less than 50 copies/ml was achieved in more patients in group B and C than in group A (68.2%, 69% vs. 39.7%; p<0.001). In planned subgroup analyses, the decrease of viral response rate was seen in group A when CD4 cell count >200/ul (subgroup H). But in subgroup L, viral response rate of three groups has no significant statistic difference. There were no statistically significant differences among three groups in immunological response within any of the CD4 or pVL strata. 3 out of 193 patients with available genotype at baseline showed primary drug resistant. Of 26 patients with virologic failure, 17 patients showed secondary drug resistant, 16 subjects in group A and 1 subject in group B. Logistic regression analysis indicated that presence of hepatotoxicity was associated with HCV-Ab positive (OR = 2.096, 95%CI: 1.106-3.973, P = 0.023) and higher CD4 baseline (CD4 count >250/ul) (OR = 2.096, 95%CI: 1.07-4.107, P = 0.031).
Conclusion: Our findings strongly support the use of 3TC+d4T and 3TC+AZT as the nucleoside analogue combination in NVP-based antiretroviral therapy. The regimen of AZT+ddI+NVP produced poor virological response especially in the stratum of CD4 count more than 200/ul. More patients showed secondary drug resistant in this arm too. Patients with HCV-Ab+ and CD4 count >250/ul appear to have significantly high risk of hepatoxicity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00618176.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Autran B, Carcelain G, Li TS, Blanc C, Mathez D, Tubiana R, et al. Positive effects of combined antiretroviral therapy on CD4+ T cell homeostasis and function in advanced HIV disease. Science. 1997;277:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JohnA, Fath MichaelJ, Demasi Ralph, Hermes Ashwaq, Quinn Joseph, et al. An updated systematic overview of triple combination therapy in antiretroviral-naïve HIV-infected adults. AIDS. 2006;20:2051–2064. - PubMed
-
- Chinese Government Official Web Portal. 650,000 HIV Victims in China: Assessment. 2006. Available at http://english.gov.cn/2006-01/25/content_171150.htm. Accessed May 15, 2007.
-
- Xinhuanet. What is “Four Free, One Care”? 2004. Available at http://news.xinhuanet.com/newscenter/2004-12/01/content_2281179.htm. Accessed May 15, 2007.
-
- Division of AIDS table for grading the severity of adult and pediatric adverse events. 2004. Available at http://rcc.tech-res.com/tox_tables.htm. Accessed May 7, 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

