Heat shock protein 90 inhibition abrogates hepatocellular cancer growth through cdc2-mediated G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
- PMID: 19082595
- PMCID: PMC4122215
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-008-0888-2
Heat shock protein 90 inhibition abrogates hepatocellular cancer growth through cdc2-mediated G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
Abstract
Purpose: 17-(demethoxy), 17-allylamino geldanamycin (17-AAG) suppresses growth in some cancers by inhibiting Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). We examined the effects of 17-AAG-mediated Hsp90 inhibition on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth in vitro and in vivo.
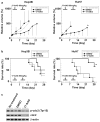
Methods: Human HCC cell lines, Hep3B and HuH7, were exposed to 17-AAG and cell viabilities and apoptosis were determined. Cell cycle profiles were analyzed and the G(2)/M cell cycle checkpoint proteins cdc2 and cyclin B1 were examined. Studies were performed to determine whether 17-AAG-mediated cdc2 decrease was due to altered gene expression, transcription, or protein degradation. The effects of 17-AAG on Hep3B and HuH7 xenograft growth in athymic nude mice were also examined.
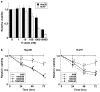
Results: Hep3B and HuH7 treated with 17-AAG versus untreated controls showed decreased cell viability and increased apoptosis. Cells treated with 17-AAG also showed an increased fraction in G(2)/M phase and an associated decrease in cdc2 through protein degradation rather than through other mechanisms. Hsp90 inhibition by 17-AAG also decreased HCC xenograft growth in association with decreased cdc2 expression.
Conclusions: 17-AAG-mediated inhibition of Hsp90 abrogates human HCC cell growth in vitro and in vivo through cdc2 decrease, which in turn induces G(2)/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Hsp90 is a mediator of HCC growth and survival and its inhibition may serve as a potential treatment.
Figures


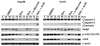
References
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, et al. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5–S16. - PubMed
-
- Welch WJ, Feramisco JR. Purification of the major mammalian heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:14949–14959. - PubMed
-
- Luk JM, Lam CT, Siu AF, et al. Proteomic profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese cohort reveals heat-shock proteins (Hsp27, Hsp70, GRP78) up-regulation and their associated prognostic values. Proteomics. 2006;6:1049–1057. - PubMed
-
- Calvisi DF, Pascale RM, Feo F. Dissection of signal transduction pathways as a tool for the development of targeted therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2007;2:217–236. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

