Immediate and delayed consequences of xanomeline wash-resistant binding at the M3 muscarinic receptor
- PMID: 19082883
- PMCID: PMC3752336
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-008-9886-3
Immediate and delayed consequences of xanomeline wash-resistant binding at the M3 muscarinic receptor
Abstract
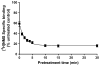
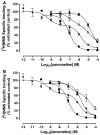
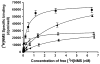
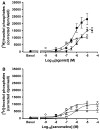
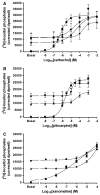
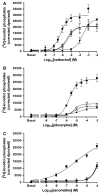
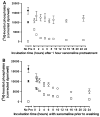
Xanomeline is thought to be a M1/M4 functionally selective agonist at muscarinic receptors. We have previously demonstrated that it binds in a unique manner at the M1 receptor. In the current study, we examined the ability of xanomeline to bind to the M3 receptor and determined the long-term consequences of this mode of binding in Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing M3 receptors. Xanomeline binds in a reversible and wash-resistant manner at the M3 receptor and elicits a functional response under both conditions. Long-term exposure to xanomeline resulted in changes in the binding profile of [(3)H]NMS and a decrease in cell-surface receptor density. Additionally, pretreatment with xanomeline was associated with antagonism of the functional response to subsequent stimulation by conventional agonists. Our results indicate that xanomeline binds to and activates the M3 muscarinic receptor in a wash-resistant manner, and that this type of binding results in time-dependent receptor regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ. International union of pharmacology Xvii. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Wess J. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice: novel phenotypes and clinical implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:423–450. 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802. 121622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

