Polymer-based sustained-release dosage forms for protein drugs, challenges, and recent advances
- PMID: 19085110
- PMCID: PMC2628253
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-008-9148-3
Polymer-based sustained-release dosage forms for protein drugs, challenges, and recent advances
Abstract
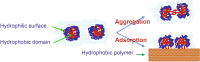
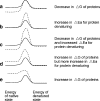
While the concept of using polymer-based sustained-release delivery systems to maintain therapeutic concentration of protein drugs for extended periods of time has been well accepted for decades, there has not been a single product in this category successfully commercialized to date despite clinical and market demands. To achieve successful systems, technical difficulties ranging from protein denaturing during formulation process and the course of prolonged in vivo release, burst release, and incomplete release, to low encapsulation efficiency and formulation complexity have to be simultaneously resolved. Based on this updated understanding, formulation strategies attempting to address these aspects comprehensively were reported in recent years. This review article (with 134 citations) aims to summarize recent studies addressing the issues above, especially those targeting practical industrial solutions. Formulation strategies representative of three areas, microsphere technology using degradable hydrophobic polymers, microspheres made of water soluble polymers, and hydrophilic in vivo gelling systems will be selected and introduced. To better understand the observations and conclusions from different studies for different systems and proteins, physicochemical basis of the technical challenges and the pros and cons of the corresponding formulation methods will be discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Frokjaer S., Otzen D. E. Protein drugs stability: a formulation challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:298–306. - PubMed
-
- Wang W. Lyophilization and development of solid protein pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. 2000;203:1–60. - PubMed
-
- Marc S., Juergen S., Hennink W. E., Wim J. Recombinant gelatin hydrogels for the sustained release of proteins. J. Control Release. 2007;119:301–312. - PubMed
-
- Jeong B., Bae Y. H., Lee D. S., Kim S. W. Biodegradable copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature. 1997;388(28):860–862. - PubMed
-
- Jostel A., Mukherjee A., Alenfall J., Smethurst L., Shalet S. M. A new sustained-release preparation of human growth hormone and its pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and safety profile. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005;62:623–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous