Critical role of IkappaB kinase alpha in embryonic skin development and skin carcinogenesis
- PMID: 19085841
- PMCID: PMC7243875
- DOI: 10.14670/HH-24.265
Critical role of IkappaB kinase alpha in embryonic skin development and skin carcinogenesis
Abstract
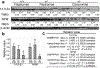
IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha), IKKbeta, and IKKgamma/NEMO form the IKK complex, which is essential for NF-kappaB activation. However, genetic studies have shown that the role of IKKalpha is distinct from that of IKKbeta or IKKgamma in the development of the mouse embryonic skin. Loss of IKKalpha has been shown to cause epidermal hyperplasia, prevent keratinocyte terminal differentiation, and impair the formation of the skin, resulting in the deaths of IKKalpha-deficient (Ikkalpha-/-) mice soon after birth. Recent experimental data from several laboratories have revealed that IKKalpha functions as a tumor suppressor in human squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of skin, lungs, and head and neck. Chemical carcinogenesis studies using mice have shown that reduction in IKKalpha expression increases the number and size of Ras-initiated skin tumors and promotes their progression, indicating that reduced IKKalpha expression provides a selective growth advantage that cooperates with Ras activity to promote skin carcinogenesis. In this review, we will summarize these findings from our and other studies on the role that IKKalpha plays in development of the mouse embryonic skin and skin carcinogenesis.
Figures
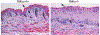
References
-
- Aldaz CM, Conti CJ, Larcher F, Trono D, Roop DR, Chesner J, Whitehead T. and Slaga TJ (1988). Sequential development of aneuploidy, keratin modifications, and gamma-glutamyltransferase expression in mouse skin papillomas. Cancer Res. 48, 3253–3257. - PubMed
-
- Balmain A. and Pragnell IB (1983). Mouse skin carcinomas induced in vivo by chemical carcinogens have a transforming Harvey-ras oncogene. Nature 303, 72–74. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau D. and Longy M. (2000). Mutations of the human PTEN gene. Hum. Mutat 16, 109–122. - PubMed
-
- Candi E, Terrinoni A, Rufini A, Chikh A, Lena AM, Suzuki Y, Sayan BS, Knight RA and Melin G. (2006). p63 is upstream of IKK alpha in epidermal development. J. Cell. Sci 119, 4617–4622. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Bonizzi G, Seagroves TN, Greten FR, Johnson R, Schmidt EV and Karin M. (2001). IKKα provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin 01 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 107, 763–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
