Annotating genomes with massive-scale RNA sequencing
- PMID: 19087247
- PMCID: PMC2646279
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-12-r175
Annotating genomes with massive-scale RNA sequencing
Abstract
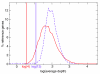
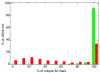
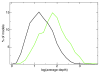
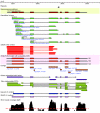
Next generation technologies enable massive-scale cDNA sequencing (so-called RNA-Seq). Mainly because of the difficulty of aligning short reads on exon-exon junctions, no attempts have been made so far to use RNA-Seq for building gene models de novo, that is, in the absence of a set of known genes and/or splicing events. We present G-Mo.R-Se (Gene Modelling using RNA-Seq), an approach aimed at building gene models directly from RNA-Seq and demonstrate its utility on the grapevine genome.
Figures

References
-
- Korbel JO, Urban AE, Grubert F, Du J, Royce TE, Starr P, Zhong G, Emanuel BS, Weissman SM, Snyder M, Gerstein MB. Systematic prediction and validation of breakpoints associated with copy-number variants in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:10110–10115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703834104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Kalscheuer V, Tzschach A, Menzel C, Ullmann R, Schulz MH, Erdogan F, Li N, Kijas Z, Arkesteijn G, Pajares IL, Goetz-Sothmann M, Heinrich U, Rost I, Dufke A, Grasshoff U, Glaeser B, Vingron M, Ropers HH. Mapping translocation breakpoints by next-generation sequencing. Genome Res. 2008;18:1143–1149. doi: 10.1101/gr.076166.108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

