miR-519 reduces cell proliferation by lowering RNA-binding protein HuR levels
- PMID: 19088191
- PMCID: PMC2629338
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809376106
miR-519 reduces cell proliferation by lowering RNA-binding protein HuR levels
Abstract
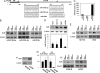
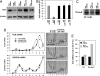
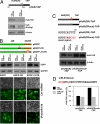
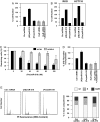
Gene expression is potently regulated through the action of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). Here, we present evidence of a miRNA regulating an RBP. The RBP HuR can stabilize and modulate the translation of numerous target mRNAs involved in cell proliferation, but little is known about the mechanisms that regulate HuR abundance. We identified two putative sites of miR-519 interaction on the HuR mRNA, one in its coding region (CR), one in its 3'-untranslated region (UTR). In several human carcinoma cell lines tested, HeLa (cervical), HCT116 and RKO (colon), and A2780 (ovarian), overexpression of a miR-519 precursor [(Pre)miR-519] reduced HuR abundance, while inhibiting miR-519 by using an antisense RNA [(AS)miR-519] elevated HuR levels. The influence of miR-519 was recapitulated using heterologous reporter constructs that revealed a greater repressive effect on the HuR CR than the HuR 3'-UTR target sequences. miR-519 did not alter HuR mRNA abundance, but reduced HuR biosynthesis, as determined by measuring nascent HuR translation and HuR mRNA association with polysomes. Modulation of miR-519 leading to altered HuR levels in turn affected the levels of proteins encoded by HuR target mRNAs. In keeping with HuR's proliferative influence, (AS)miR-519 significantly increased cell number and [(3)H]-thymidine incorporation, while (Pre)miR-519 reduced these parameters. Importantly, the growth-promoting effects of (AS)miR-519 required the presence of HuR, because downregulation of HuR by RNAi dramatically suppressed its proliferative action. In sum, miR-519 represses HuR translation, in turn reducing HuR-regulated gene expression and cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Competitive regulation of nucleolin expression by HuR and miR-494.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Oct;31(20):4219-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05955-11. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21859890 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of Wnt co-receptor LRP6 and RNA-binding protein HuR by miR-29b in intestinal epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2016 Jun 1;473(11):1641-9. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160057. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27089893 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of repression of HuR translation by miR-16 may be responsible for the elevation of HuR in human breast carcinoma.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Oct 15;111(3):727-34. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22762. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20626035
-
Properties of the Regulatory RNA-Binding Protein HuR and its Role in Controlling miRNA Repression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;700:106-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7823-3_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21755477 Review.
-
Properties of the regulatory RNA-binding protein HuR and its role in controlling miRNA repression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;700:106-23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21627034 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-Binding Proteins in Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 26;21(11):3757. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113757. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32466553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A common single-nucleotide polymorphism in cyclooxygenase-2 disrupts microRNA-mediated regulation.Oncogene. 2012 Mar 22;31(12):1592-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.349. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21822307 Free PMC article.
-
Why West? Comparisons of clinical, genetic and molecular features of infants with and without spasms.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 8;13(3):e0193599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193599. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29518120 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug efflux transporter ABCG2: expression and regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):6887-6939. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03901-y. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34586444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Mechanisms of the Development of Neocortical Lamination.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Nov 9;11:102. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00102. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29170632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keene JD. RNA regulons: coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. 2005;309:1514–1518. - PubMed
-
- Abdelmohsen K, Lal A, Kim HH, Gorospe M. Posttranscriptional orchestration of an anti-apoptotic program by HuR. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:1288–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

