Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1)
- PMID: 19088198
- PMCID: PMC2634900
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810958105
Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1)
Abstract
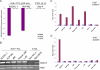
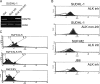
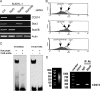
The mechanisms of malignant cell transformation caused by the oncogenic, chimeric nucleophosmin (NPM)/anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) remain only partially understood, with most of the previous studies focusing mainly on the impact of NPM/ALK on cell survival and proliferation. Here we report that the NPM/ALK-carrying T cell lymphoma (ALK+TCL) cells strongly express the immunosuppressive cell-surface protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1), as determined on the mRNA and protein level. The CD274 expression is strictly dependent on the expression and enzymatic activity of NPM/ALK, as demonstrated by inhibition of the NPM/ALK function in ALK+TCL cells by the small molecule ALK inhibitor CEP-14083 and by documenting CD274 expression in IL-3-depleted BaF3 cells transfected with the wild-type NPM/ALK, but not the kinase-inactive NPM/ALK K210R mutant or empty vector alone. NPM/ALK induces CD274 expression by activating its key signal transmitter, transcription factor STAT3. STAT3 binds to the CD274 gene promoter in vitro and in vivo, as shown in the gel electromobility shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, and is required for the PD-L1 gene expression, as demonstrated by siRNA-mediated STAT3 depletion. These findings identify an additional cell-transforming property of NPM/ALK and describe a direct link between an oncoprotein and an immunosuppressive cell-surface protein. These results also provide an additional rationale to therapeutically target NPM/ALK and STAT3 in ALK+TCL. Finally, they suggest that future immunotherapeutic protocols for this type of lymphoma may need to include the inhibition of NPM/ALK and STAT3 to achieve optimal clinical efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li R, Morris SW. Development of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) small-molecule inhibitors for cancer therapy. Med Res Rev. 2008;28:372–412. - PubMed
-
- Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–1284. - PubMed
-
- Shiota M, et al. Hyperphosphorylation of a novel 80 kDa protein-tyrosine kinase similar to Ltk in a human Ki-1 lymphoma cell line, S3. Oncogene. 1994;9:1567–1574. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, et al. ALK, the chromosome 2 gene locus altered by the t (2; 5) in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, encodes a novel neural receptor tyrosine kinase that is highly related to leukocyte tyrosine kinase (LTK) Oncogene. 1997;14:2175–2188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

