Inhibition of mRNA export and dimerization of interferon regulatory factor 3 by Theiler's virus leader protein
- PMID: 19088287
- PMCID: PMC2632858
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.005678-0
Inhibition of mRNA export and dimerization of interferon regulatory factor 3 by Theiler's virus leader protein
Abstract
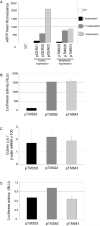
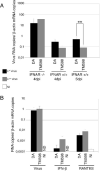
Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV or Theiler's virus) is a neurotropic picornavirus that can persist lifelong in the central nervous system of infected mice, causing a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease. The leader (L) protein of the virus is an important determinant of viral persistence and has been shown to inhibit transcription of type I interferon (IFN) genes and to cause nucleocytoplasmic redistribution of host proteins. In this study, it was shown that expression of the L protein shuts off synthesis of the reporter proteins green fluorescent protein and firefly luciferase, suggesting that it induces a global shut-off of host protein expression. The L protein did not inhibit transcription or translation of the reporter genes, but blocked cellular mRNA export from the nucleus. This activity correlated with the phosphorylation of nucleoporin 98 (Nup98), an essential component of the nuclear pore complex. In contrast, the data confirmed that the L protein inhibited IFN expression at the transcriptional level, and showed that transcription of other chemokine or cytokine genes was affected by the L protein. This transcriptional inhibition correlated with inhibition of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3) dimerization. Whether inhibition of IRF-3 dimerization and dysfunction of the nuclear pore complex are related phenomena remains an open question. In vivo, IFN antagonism appears to be an important role of the L protein early in infection, as a virus bearing a mutation in the zinc finger of the L protein replicated as efficiently as the wild-type virus in type I IFN receptor-deficient mice, but had impaired fitness in IFN-competent mice.
Figures


References
-
- Blevins MB, Smith AM, Phillips EM, Powers MA. Complex formation among the RNA export proteins Nup98, Rae1/Gle2, and TAP. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:20979–20988. - PubMed
-
- Brahic M, Bureau JF, Michiels T. The Genetics of the Persistent Infection and Demyelinating Disease Caused by Theiler’s Virus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty P, Satterly N, Fontoura BM. Nuclear export assays for poly(A) RNAs. Methods. 2006;39:363–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

