An orphan LuxR homolog of Sinorhizobium meliloti affects stress adaptation and competition for nodulation
- PMID: 19088317
- PMCID: PMC2643561
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01692-08
An orphan LuxR homolog of Sinorhizobium meliloti affects stress adaptation and competition for nodulation
Abstract
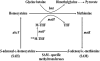
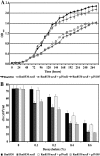
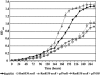
The Sin/ExpR quorum-sensing system of Sinorhizobium meliloti plays an important role in the symbiotic association with its host plant, Medicago sativa. The LuxR-type response regulators of the Sin system include the synthase (SinI)-associated SinR and the orphan regulator ExpR. Interestingly, the S. meliloti Rm1021 genome codes for four additional putative orphan LuxR homologs whose regulatory roles remain to be identified. These response regulators contain the characteristic domains of the LuxR family of proteins, which include an N-terminal autoinducer/response regulatory domain and a C-terminal helix-turn-helix domain. This study elucidates the regulatory role of one of the orphan LuxR-type response regulators, NesR. Through expression and phenotypic analyses, nesR was determined to affect the active methyl cycle of S. meliloti. Moreover, nesR was shown to influence nutritional and stress response activities in S. meliloti. Finally, the nesR mutant was deficient in competing with the wild-type strain for plant nodulation. Taken together, these results suggest that NesR potentially contributes to the adaptability of S. meliloti when it encounters challenges such as high osmolarity, nutrient starvation, and/or competition for nodulation, thus increasing its chances for survival in the stressful rhizosphere.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The LuxR homolog ExpR, in combination with the Sin quorum sensing system, plays a central role in Sinorhizobium meliloti gene expression.J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(16):5460-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.16.5460-5472.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15292148 Free PMC article.
-
A LuxR homolog controls production of symbiotically active extracellular polysaccharide II by Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5067-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.18.5067-5076.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12193623 Free PMC article.
-
ExpR coordinates the expression of symbiotically important, bundle-forming Flp pili with quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Apr;80(8):2429-39. doi: 10.1128/AEM.04088-13. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24509921 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of motility by the ExpR/Sin quorum-sensing system in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):861-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.01310-07. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18024512 Free PMC article.
-
Role of quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti-Alfalfa symbiosis.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jul;191(13):4372-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.00376-09. Epub 2009 Apr 24. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19395488 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bacterial LuxR solos have evolved to respond to different molecules including signals from plants.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Nov 12;4:447. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00447. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24273546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A LuxR-type regulator, AcrR, regulates flagellar assembly and contributes to virulence, motility, biofilm formation, and growth ability of Acidovorax citrulli.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Apr;21(4):489-501. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12910. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31943660 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii rosR is required for interaction with clover, biofilm formation and adaptation to the environment.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Nov 11;10:284. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-284. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21070666 Free PMC article.
-
The kiwifruit emerging pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae does not produce AHLs but possesses three luxR solos.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e87862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087862. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498215 Free PMC article.
-
Silent signals: how N-acyl homoserine lactones drive oral microbial behaviour and health outcomes.Front Oral Health. 2024 Dec 5;5:1484005. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1484005. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39703871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbas, B. A., K. E. Vineetha, C. K. Prasad, N. Vij, R. Hassani, and G. S. Randhawa. 2002. Symbiotic characteristics of cysteine and methionine auxotrophs of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 40:1121-1130. - PubMed
-
- Ahmer, B. M. 2004. Cell-to-cell signalling in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. Mol. Microbiol. 52:933-945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

