Calcium signaling in immune cells
- PMID: 19088738
- PMCID: PMC2877033
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.f.220
Calcium signaling in immune cells
Erratum in
- Nat Immunol. 2009 Feb;10(2):223
Abstract
Calcium acts as a second messenger in many cell types, including lymphocytes. Resting lymphocytes maintain a low concentration of Ca2+. However, engagement of antigen receptors induces calcium influx from the extracellular space by several routes. A chief mechanism of Ca2+ entry in lymphocytes is through store-operated calcium (SOC) channels. The identification of two important molecular components of SOC channels, CRACM1 (the pore-forming subunit) and STIM1 (the sensor of stored calcium), has allowed genetic and molecular manipulation of the SOC entry pathway. In this review, we highlight advances in the understanding of Ca2+ signaling in lymphocytes with special emphasis on SOC entry. We also discuss outstanding questions and probable future directions of the field.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at
Figures
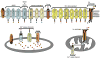

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

