Gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia: discrepancies between direct and indirect meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 19089502
- PMCID: PMC2628998
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-008-0877-5
Gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia: discrepancies between direct and indirect meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials
Erratum in
- J Gen Intern Med. 2009 Oct;24(10):1172
Abstract
Background: Previous systematic reviews concluded that tricyclics antidepressants are superior to gabapentin for neuropathic pain, but were based on indirect comparisons from placebo-controlled trials.
Purpose: To evaluate gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia, using direct and indirect comparisons.
Data sources: MEDLINE (1966 to March Week 4 2008), the Cochrane central register of controlled trials (1st quarter 2008), and reference lists.
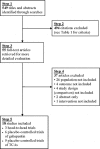
Study selection: We selected randomized trials directly comparing gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants or comparing either of these medications versus placebo.
Data extraction: Studies were reviewed, abstracted, and quality-rated by two independent investigators using predefined criteria.
Data synthesis: We performed a meta-analysis of head-to-head trials using a random effects model and compared the results to an adjusted indirect analysis of placebo-controlled trials.
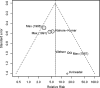
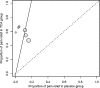
Results: In three head-to-head trials, there was no difference between gabapentin and tricyclic antidepressants for achieving pain relief (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.29). In adjusted indirect analyses, gabapentin was worse than tricyclic antidepressants for achieving pain relief (RR = 0.41, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.74). The discrepancy between direct and indirect analyses was statistically significant (p = 0.008). Placebo-controlled tricyclic trials were conducted earlier than the gabapentin trials, reported lower placebo response rates, had more methodological shortcomings, and were associated with funnel plot asymmetry.
Conclusions: Though direct evidence is limited, we found no difference in likelihood of achieving pain relief between gabapentin and tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia. Indirect analyses that combine data from sets of trials conducted in different eras can be unreliable.
Figures



Comment in
-
Gabapentin versus tricyclics for neuropathic pain.J Gen Intern Med. 2009 Jun;24(6):780-1; author reply 782. doi: 10.1007/s11606-009-0957-1. J Gen Intern Med. 2009. PMID: 19350332 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

