Measurement of HIV prevention indicators: a comparison of the PLACE method and a household survey in Zambia
- PMID: 19089607
- PMCID: PMC3966068
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-008-9505-y
Measurement of HIV prevention indicators: a comparison of the PLACE method and a household survey in Zambia
Abstract
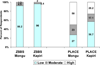
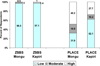
Reaching populations at greatest risk for acquiring HIV is essential for efforts to combat the epidemic. This paper presents, the Priorities for Local AIDS Control Efforts (PLACE) method which focuses on understanding the venues where people are meeting new sexual partners and behaviors which put people at risk. A comparison of data from two PLACE studies in Zambia with a national household survey, the Zambia Sexual Behavior Survey 2005, indicated that the PLACE population was at greater risk of acquiring HIV. Respondents in the two PLACE studies were significantly more likely to report 1+ new partners in the past 4 weeks, 2+ partners in the past 12 months, 1+ new partner in the past 12 months and transactional sex. Data from the PLACE method is important for targeting interventions for those most likely to acquire and transmit HIV.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson R. The transmission dynamics of sexually transmitted diseases: The behavioral components. In: Wasserheit J, Arol S, Holmes K, editors. Research Issues in Human Behavior and Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the AIDS Era. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1991. pp. 38–60.
-
- Central Statistical Office (CSO) [Zambia] HIV/AIDS Epidemiological Projections 1985–2010. Lusaka, Zambia: Central Statistical Office, Government of Zambia; 2005.
-
- Central Statistical Office (CSO) [Zambia] and MEASURE Evaluation. Sexual Behaviour Survey 2005. Chapel Hill, NC, USA: Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous