RNA under attack: cellular handling of RNA damage
- PMID: 19089684
- PMCID: PMC2656420
- DOI: 10.1080/10409230802594043
RNA under attack: cellular handling of RNA damage
Abstract
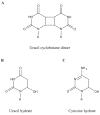
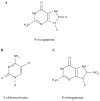
Damage to RNA from ultraviolet light, oxidation, chlorination, nitration, and akylation can include chemical modifications to nucleobases as well as RNA-RNA and RNA-protein crosslinking. In vitro studies have described a range of possible damage products, some of which are supported as physiologically relevant by in vivo observations in normal growth, stress conditions, or disease states. Damage to both messenger RNA and noncoding RNA may have functional consequences, and work has begun to elucidate the role of RNA turnover pathways and specific damage recognition pathways in clearing cells of these damaged RNAs.
Figures
References
-
- Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PO, Vagbo CB, Skorpen F, Akbari M, Sundheim O, Bjoras M, Slupphaug G, Seeberg E, et al. Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature. 2003;421:859–863. - PubMed
-
- Ambach W, Blumthaler M. Biological effectiveness of solar UV radiation in humans. Experientia. 1993;49:747–53. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules: the tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:141–150. - PubMed
-
- Badouard C, Masuda M, Nishino H, Cadet J, Favier A, Ravanat JL. Detection of chlorinated DNA and RNA nucleosides by HPLC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry as potential biomarkers of inflammation. Journal of Chromatogr B. 2005;827:26–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
