Downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and induction of tumor dormancy by 15-lipoxygenase-2 in prostate cancer
- PMID: 19089921
- PMCID: PMC2913418
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24118
Downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and induction of tumor dormancy by 15-lipoxygenase-2 in prostate cancer
Abstract
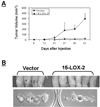
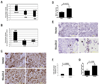
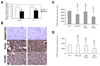
The enzyme 15-lipoxygenase-2 (15-LOX-2) utilizes arachidonic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, to synthesize 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Abundantly expressed in normal prostate epithelium but frequently suppressed in the cancerous tissues, 15-LOX-2 has been suggested as a functional suppressor of prostate cancer, but the mechanism(s) involved remains unknown. To study the functional role of 15-LOX-2 in prostate cancer, we expressed 15-LOX-2 as a fusion protein with GFP in DU145 and PC-3 cells and found that 15-LOX-2 increased cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. When injected into athymic nu/nu mice, prostate cancer cells with 15-LOX-2 expression could still form palpable tumors without significant changes in tumorigenicity. But, the tumors with 15-LOX-2 expression grew significantly slower than those derived from vector controls and were kept dormant for a long period of time. Histological evaluation revealed an increase in cell death in tumors derived from prostate cancer cells with 15-LOX-2 expression, while in vitro cell culture conditions, no such increase in apoptosis was observed. Further studies found that the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) was significantly reduced in prostate cancer cells with 15-LOX-2 expression restored. Our studies suggest that 15-LOX-2 suppresses VEGF gene expression and sustains tumor dormancy in prostate cancer. Loss of 15-LOX-2 functionalities, therefore, represents a key step for prostate cancer cells to exit from dormancy and embark on malignant progression in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, Kalluri R. Cancer without disease. Nature. 2004;427:787. - PubMed
-
- Sakr WA, Ward C, Grignon DJ, Haas GP. Epidemiology and molecular biology of early prostatic neoplasia. Mol Urol. 2000;4:109–113. discussion 15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

