Children with endemic Burkitt lymphoma are deficient in EBNA1-specific IFN-gamma T cell responses
- PMID: 19089927
- PMCID: PMC2708320
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24014
Children with endemic Burkitt lymphoma are deficient in EBNA1-specific IFN-gamma T cell responses
Abstract
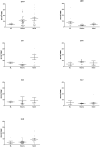
Endemic Burkitt lymphoma (eBL) is the most common childhood cancer in equatorial Africa and is linked to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Plasmodium falciparum coinfections early in life. Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) is the sole viral latent antigen expressed in BL tumors. Loss of EBNA1-specific immune surveillance could allow eBL emergence. Therefore, EBNA1-specific T cell responses were analyzed by IFN-gamma ELISPOT in Kenyan children with eBL and compared to healthy children with divergent malaria exposure. Significantly fewer children with eBL, 16% (7/44) had EBNA1-specific IFN-gamma responses in contrast to healthy children living in a malaria holoendemic area or in an area with sporadic malaria transmission, 67% (40/60) and 72% (43/60) responders, respectively (p < 0.003). Children with eBL maintained IgG(1) dominated antibody responses to EBNA1 similar to healthy children suggesting a selective loss of IFN-gamma secreting EBNA1-specific T cells in the presence of intact humoral immunity. CD8(+) T cell responses to EBV lytic and latent antigens not expressed in the tumors were similarly robust in eBL patients compared to healthy children. In addition, CD4(+) T cell responses to a malaria protein, merozoite surface protein 1, were present in lymphoma patients. This study demonstrates a selective loss of EBNA1-specific T cell responses in children with eBL and suggests a potential immunotherapeutic target for this EBV-associated lymphoma.
Figures

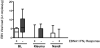
References
-
- Crawford DH. Biology and disease associations of Epstein-Barr virus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001. pp. 461–73. 2001;356(1408):461-73. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mwanda OW, Rochford R, Moormann AM, MacNeil A, Whalen C, Wilson ML. Burkitt's lymphoma in Kenya: geographical, age, gender and ethnic distribution. East Afr Med J. 2004. pp. S68–77. 2004(8 Suppl):S68-77. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Moormann AM, Chelimo K, Sumba PO, Tisch DJ, Rochford R, Kazura JW. Exposure to holoendemic malaria results in suppression of Epstein-Barr virus-specific T cell immunosurveillance in Kenyan children. J Infect Dis. 2007. pp. 799–808. 2007;195(6):799-808. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Blake N, Lee S, Redchenko I, Thomas W, Steven N, Leese A, Steigerwald-Mullen P, Kurilla MG, Frappier L, Rickinson A. Human CD8+ T cell responses to EBV EBNA1: HLA class I presentation of the (Gly-Ala)-containing protein requires exogenous processing. Immunity. 1997. pp. 791–802. 1997;7(6):791-802. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Levitskaya J, Coram M, Levitsky V, Imreh S, Steigerwald-Mullen PM, Klein G, Kurilla MG, Masucci MG. Inhibition of antigen processing by the internal repeat region of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1. Nature. 1995. pp. 685–8. 1995;375(6533):685-8. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- D43 TW006576/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA189806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA101741/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI051565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA101741/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA108609/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA108609/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI4390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043906/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043906/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW006576-05/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- K08-AI51565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

