Molecular genetics of ameloblast cell lineage
- PMID: 19090561
- PMCID: PMC2737325
- DOI: 10.1002/jez.b.21261
Molecular genetics of ameloblast cell lineage
Abstract
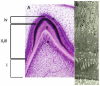
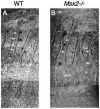
Late tooth morphogenesis is characterized by a series of events that determine crown morphogenesis and the histodifferentiation of epithelial cells into enamel-secreting ameloblasts and of mesenchymal cells into dentin-secreting odontoblasts. Functional ameloblasts are tall, columnar, polarized cells that synthesize and secrete a number of enamel-specific proteins. After depositing the full thickness of enamel matrix, ameloblasts shrink in size and regulate enamel maturation. Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a heterogeneous group of inherited defects in enamel formation. Clinically, AI presents as a spectrum of enamel malformations that are categorized as hypoplastic, hypocalcified, or hypomaturation types, based upon the thickness and hardness of the enamel. The different types of AI are inherited, either as X-linked, autosomal-dominant, or autosomal-recessive traits. Recently, several gene mutations have been identified to cause the subtypes of AI. How these genes, however, coordinate their function to control amelogenesis is not understood. In this review, we discuss the role of genes that play definitive role on the determination of ameloblast cell fate and life cycle based on studies in transgenic animals.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Aberdam D, Aguzzi A, Baudoin C, Galliano MF, Ortonne JP, Meneguzzi G. Developmental expression of nicein adhesion protein (laminin-5) subunits suggests multiple morphogenic roles. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1994;2:115–129. - PubMed
-
- Aldred MJ, Savarirayan R, Crawford PJ. Amelogenesis imperfecta: a classification and catalogue for the 21st century. Oral Dis. 2003;9(1):19–23. - PubMed
-
- Baker SE, Hopkinson SB, Fitchmun M, Andreason GL, Frasier F, Plopper G, Quaranta V, Jones JC. Laminin-5 and hemidesmosomes: role of the alpha 3 chain subunit in hemidesmosome stability and assembly. J. Cell Sci. 1996;109:2509–2520. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JD, Beniash E, Lee DH, Smith CE. Decreased mineral content in MMP-20 null mouse enamel is prominent during the maturation stage. J. Dent. Res. 2004;83:909–913. - PubMed
-
- Begue-Kirn C, Krebsbach PH, Bartlett JD, Butler WT. Dentin sialoprotein, dentin phosphoprotein, enamelysin and ameloblastin: tooth-specific molecules that are distinctively expressed during murine dental differentiation. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998;106(5):963–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

