SUMO-specific protease 2 is essential for modulating p53-Mdm2 in development of trophoblast stem cell niches and lineages
- PMID: 19090619
- PMCID: PMC2602722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060310
SUMO-specific protease 2 is essential for modulating p53-Mdm2 in development of trophoblast stem cell niches and lineages
Abstract
SUMO-specific protease 2 (SENP2) modifies proteins by removing SUMO from its substrates. Although SUMO-specific proteases are known to reverse sumoylation in many defined systems, their importance in mammalian development and pathogenesis remains largely elusive. Here we report that SENP2 is highly expressed in trophoblast cells that are required for placentation. Targeted disruption of SENP2 in mice reveals its essential role in development of all three trophoblast layers. The mutation causes a deficiency in cell cycle progression. SENP2 has a specific role in the G-S transition, which is required for mitotic and endoreduplication cell cycles in trophoblast proliferation and differentiation, respectively. SENP2 ablation disturbs the p53-Mdm2 pathway, affecting the expansion of trophoblast progenitors and their maturation. Reintroducing SENP2 into the mutants can reduce the sumoylation of Mdm2, diminish the p53 level and promote trophoblast development. Furthermore, downregulation of p53 alleviates the SENP2-null phenotypes and stimulation of p53 causes abnormalities in trophoblast proliferation and differentiation, resembling those of the SENP2 mutants. Our data reveal a key genetic pathway, SENP2-Mdm2-p53, underlying trophoblast lineage development, suggesting its pivotal role in cell cycle progression of mitosis and endoreduplication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

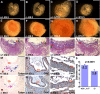
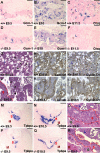


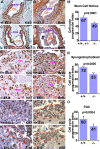
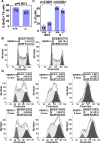

Comment in
-
Lessons on life from SENP2.PLoS Biol. 2008 Dec;6(12):e312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060312. Epub 2008 Dec 16. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 20076701 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rossant J, Cross JC. Placental development: lessons from mouse mutants. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:538–548. - PubMed
-
- Simmons DG, Cross JC. Determinants of trophoblast lineage and cell subtype specification in the mouse placenta. Dev Biol. 2005;284:12–24. - PubMed
-
- Sutherland A. Mechanisms of implantation in the mouse: differentiation and functional importance of trophoblast giant cell behavior. Dev Biol. 2003;258:241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

