WSPMaker: a web tool for calculating selection pressure in proteins and domains using window-sliding
- PMID: 19091012
- PMCID: PMC2638153
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S12-S13
WSPMaker: a web tool for calculating selection pressure in proteins and domains using window-sliding
Abstract
Background: In the study of adaptive evolution, it is important to detect the protein coding sites where natural selection is acting. In general, the ratio of the rate of non-synonymous substitutions (Ka) to the rate of synonymous substitutions (Ks) is used to estimate either negative or positive selection for an entire gene region of interest. However, since each amino acid in a region has a different function and structure, the type and strength of natural selection may be different for each amino acid. Specifically, domain sites on the protein are indicative of structurally and functionally important sites. Therefore, Window-sliding tools can be used to detect evolutionary forces acting on mutation sites.
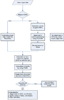
Results: This paper reports the development of a web-based tool, WSPMaker (Window-sliding Selection pressure Plot Maker), for calculating selection pressures (estimated by Ka/Ks) in the sub-regions of two protein-coding DNA sequences (CDSs). The program uses a sliding window on DNA with a user-defined window length. This enables the investigation of adaptive protein evolution and shows selective constraints of the overall/specific region(s) of two orthologous gene-coding DNA sequences. The method accommodates various evolutionary models and options such as the sliding window size. WSPmaker uses domain information from Pfam HMM models to detect highly conserved residues within orthologous proteins.
Conclusion: WSPMaker is a web tool for scanning and calculating selection pressures (estimated by Ka/Ks) in sub-regions of two protein-coding DNA sequences (CDSs).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Codon-based detection of positive selection can be biased by heterogeneous distribution of polar amino acids along protein sequences.Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2006:335-40. Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2006. PMID: 17369652 Free PMC article.
-
SWAKK: a web server for detecting positive selection in proteins using a sliding window substitution rate analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W382-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl272. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845032 Free PMC article.
-
SWAPSC: sliding window analysis procedure to detect selective constraints.Bioinformatics. 2004 Nov 1;20(16):2867-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth303. Epub 2004 May 6. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15130925
-
Can RNA selection pressure distort the measurement of Ka/Ks?Gene. 2006 Mar 29;370:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.015. Epub 2006 Feb 20. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16488091 Review.
-
Extensive purifying selection acting on synonymous sites in HIV-1 Group M sequences.Virol J. 2008 Dec 23;5:160. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-160. Virol J. 2008. PMID: 19105834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging strengths in Asia Pacific bioinformatics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Dec 12;9 Suppl 12(Suppl 12):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S12-S1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19091008 Free PMC article.
-
PSP: rapid identification of orthologous coding genes under positive selection across multiple closely related prokaryotic genomes.BMC Genomics. 2013 Dec 27;14:924. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-924. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24373418 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of complete genome sequence of Neorickettsia risticii: causative agent of Potomac horse fever.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Oct;37(18):6076-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp642. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19661282 Free PMC article.
-
Duplication, concerted evolution and purifying selection drive the evolution of mosquito vitellogenin genes.BMC Evol Biol. 2010 May 13;10:142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-142. BMC Evol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20465817 Free PMC article.
-
Testis-specific glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: origin and evolution.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Jun 10;11:160. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-160. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21663662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldman N, Yang Z. A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1994;11:725–736. - PubMed
-
- Nei M, Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986;3:418–426. - PubMed
-
- Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. New York; Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

