Ileoileal intussusception induced by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- PMID: 19091094
- PMCID: PMC2615009
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-6-133
Ileoileal intussusception induced by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Abstract
Background: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract of varying malignant potential that are believed to originate from neoplastic transformation of the interstitial cells of Cajal. They may occur anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, but most commonly arise in the stomach or small intestine. They usually grow exophytically invading adjacent organs or perforating into the peritoneal cavity. They may also cause bleeding or obstructive symptoms. Intussusception and obstruction is a very uncommon presentation of these lesions because of their tendency to grow in an exraluminal fashion.
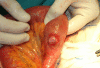
Case presentation: We present an unusual case of ileoileal intussusception in a 79-year-old female patient caused by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor located in the terminal ileum, and review the diagnostic and therapeutic approach highlighting the difficulty in diagnosing this entity preoperatively as a cause for intestinal obstruction.
Conclusion: This case presents an unusual malignant cause of adult intussusception and highlights the importance of computed tomography scanning in the accurate diagnosis of this rare entity.
Figures


References
-
- Weiss NS, Yang CP. Incidence of histologic types of cancer of the small intestine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:653–656. - PubMed
-
- Blay JY, Bonvalot S, Casali P, Choi H, Debiec-Richter M, Dei Tos AP, Emile JF, Gronchi A, Hogendoorn PC, Joensuu H, Le Cense A, McClure J, Maurel J, Nupponen N, Ray-Coquard I, Reichardt P, Sciot R, Stroobants S, van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom A, Demetri GD. GIST consensus meeting panellists. Consensus meeting for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Report of the GIST Consensus Conference of 20–21 March 2004, under the auspices of ESMO. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:566–578. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdi127. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

