Long-term actions of interleukin-1beta on delay and tonic firing neurons in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to central sensitization
- PMID: 19091115
- PMCID: PMC2625335
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-63
Long-term actions of interleukin-1beta on delay and tonic firing neurons in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to central sensitization
Abstract
Background: Cytokines such as interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) have been implicated in the development of central sensitization that is characteristic of neuropathic pain. To examine its long-term effect on nociceptive processing, defined medium organotypic cultures of rat spinal cord were exposed to 100 pM IL-1beta for 6-8 d. Interleukin effects in the dorsal horn were examined by whole-cell patch-clamp recording and Ca(2+) imaging techniques.
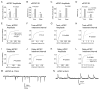
Results: Examination of the cultures with confocal Fluo-4 AM imaging showed that IL-1beta increased the change in intracellular Ca(2+) produced by exposure to 35-50 mM K+. This is consistent with a modest increase in overall dorsal horn excitability. Despite this, IL-1beta did not have a direct effect on rheobase or resting membrane potential nor did it selectively destroy any specific neuronal population. All effects were instead confined to changes in synaptic transmission. A variety of pre- and postsynaptic actions of IL-1beta were seen in five different electrophysiologically-defined neuronal phenotypes. In putative excitatory 'delay' neurons, cytokine treatment increased the amplitude of spontaneous EPSC's (sEPSC) and decreased the frequency of spontaneous IPSC's (sIPSC). These effects would be expected to increase dorsal horn excitability and to facilitate the transfer of nociceptive information. However, other actions of IL-1beta included disinhibition of putative inhibitory 'tonic' neurons and an increase in the amplitude of sIPSC's in 'delay' neurons.
Conclusion: Since spinal microglial activation peaks between 3 and 7 days after the initiation of chronic peripheral nerve injury and these cells release IL-1beta at this time, our findings define some of the neurophysiological mechanisms whereby nerve-injury induced release of IL-1beta may contribute to the central sensitization associated with chronic neuropathic pain.
Figures
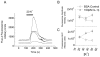
Similar articles
-
Neuron type-specific effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to 'central sensitization'.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):543-63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141267. Epub 2007 Aug 30. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17761774 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord.J Neurosci. 2008 May 14;28(20):5189-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3338-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18480275 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor drives the changes in excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat superficial dorsal horn that follow sciatic nerve injury.J Physiol. 2009 Mar 1;587(Pt 5):1013-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.166306. Epub 2009 Jan 5. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19124536 Free PMC article.
-
Is BDNF sufficient for information transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset of central sensitization?Mol Pain. 2010 Jul 23;6:44. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-44. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20653959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Molecular and Synaptic Targets for the Management of Chronic Pain Caused by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3602. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073602. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of interleukin-1 beta as a key mediator in the upregulation of Cav3.2-USP5 interactions in the pain pathway.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan-Dec;13:1744806917724698. doi: 10.1177/1744806917724698. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28741432 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine and Fentanyl Repeated Administration Induces Different Levels of NLRP3-Dependent Pyroptosis in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus of Male Rats via Cell-Specific Activation of TLR4 and Opioid Receptors.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;42(3):677-694. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00957-5. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 32926257 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral and central sensitization in remote spinal cord regions contribute to central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury.Pain. 2009 Dec 15;147(1-3):265-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.09.030. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19853381 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of gamma-linolenic acid in the formalin test in the rats.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Mar 25;86(5):2677-2683. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002001. eCollection 2024 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38694379 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain; what we know and what we should do about it.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 22;4:1220034. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1220034. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37810432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

