Regional variation in interhemispheric coordination of intrinsic hemodynamic fluctuations
- PMID: 19091966
- PMCID: PMC4113425
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4544-08.2008
Regional variation in interhemispheric coordination of intrinsic hemodynamic fluctuations
Abstract
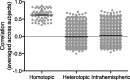
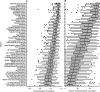
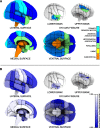
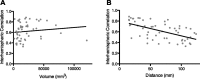
Electrophysiological studies have long demonstrated a high degree of correlated activity between the left and right hemispheres, however little is known about regional variation in this interhemispheric coordination. Whereas cognitive models and neuroanatomical evidence suggest differences in coordination across primary sensory-motor cortices versus higher-order association areas, these have not been characterized. Here, we used resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data acquired from 62 healthy volunteers to examine interregional correlation in spontaneous low-frequency hemodynamic fluctuations. Using a probabilistic atlas, we correlated probability-weighted time series from 112 regions comprising the entire cerebrum. We then examined regional variation in correlated activity between homotopic regions, contrasting primary sensory-motor cortices, unimodal association areas, and heteromodal association areas. Consistent with previous studies, robustly correlated spontaneous activity was noted between all homotopic regions, which was significantly higher than that between nonhomotopic (heterotopic and intrahemispheric) regions. We further demonstrated substantial regional variation in homotopic interhemispheric correlations that was highly consistent across subjects. Specifically, there was a gradient of interhemispheric correlation, with highest correlations across primary sensory-motor cortices (0.758, SD=0.152), significantly lower correlations across unimodal association areas (0.597, SD=0.230) and still lower correlations across heteromodal association areas (0.517, SD=0.226). These results demonstrate functional differences in interhemispheric coordination related to the brain's hierarchical subdivisions. Synchrony across primary cortices may reflect networks engaged in bilateral sensory integration and motor coordination, whereas lower coordination across heteromodal association areas is consistent with functional lateralization of these regions. This novel method of examining interhemispheric coordination may yield insights regarding diverse disease processes as well as healthy development.
Figures


References
-
- Aboitiz F, López J, Montiel J. Long distance communication in the human brain: timing constraints for inter-hemispheric synchrony and the origin of brain lateralization. Biol Res. 2003;36:89–99. - PubMed
-
- Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Fisher RS, Zaidel E. Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res. 1992;598:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Sultzer D, Lu PH, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J, Cummings JL. Heterogeneous age-related breakdown of white matter structural integrity: implications for cortical “disconnection” in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Belger A, Banich MT. Interhemispheric interaction affected by computational complexity. Neuropsychologia. 1992;30:923–929. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
