Impact of inbreeding on fertility in a pre-industrial population
- PMID: 19092776
- PMCID: PMC2986271
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.237
Impact of inbreeding on fertility in a pre-industrial population
Abstract
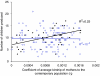
Little is known about the effects of inbreeding on reproduction in modern human societies. It appears indeed that biological effects are hidden by socioeconomic factors, which are the major determinants of fertility. It has been established, in particular, that socially induced reproductive compensation tends to homogenize the number of offspring per family in a given population. Besides, in the field of evolutionary biology, a number of empirical and theoretical studies have shown that the effects of inbreeding are condition dependent. In particular, theoretical developments on the evolution of senescence predict that the deleterious effects of inbreeding should increase with age. We rely on these developments to examine the effects of inbreeding on fertility in a cohort of Canadian women born in the late 19th century. The analysis does not allow for the detection of any effect of inbreeding on the overall number of offspring of women. However, results indicate that high levels of close father inbreeding are associated with a reduction of the productivity of parents during the second half of their reproductive period, as compared with the first half. We suggest that inbreeding depression affects reproduction in modern societies through an interaction with age.
Figures


References
-
- Fuster V. Inbreeding pattern and reproductive success in a rural community from Galicia (Spain) J Biosoc Sci. 2003;35:83–93. - PubMed
-
- Hussain R, Bittles AH. Consanguineous marriage and differentials in age at marriage, contraceptive use and fertility in Pakistan. J Biosoc Sci. 1999;31:121–138. - PubMed
-
- Hussain R, Bittles AH. Assessment of association between consanguinity and fertility in Asian populations. J Health Popul Nutr. 2004;22:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Bittles AH, Grant JC, Sullivan SG, Hussain R. Does inbreeding lead to decreased human fertility. Ann Hum Biol. 2002;29:111–130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

