Intermittent hypoxia regulates RNA polymerase II in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 19095046
- PMCID: PMC2668983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.11.025
Intermittent hypoxia regulates RNA polymerase II in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex
Abstract
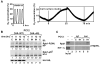
Intermittent hypoxia (IH) is a major pathological factor in the development of neural deficits associated with sleep-disordered breathing. Here we demonstrate that IH lasting 2 or 30 days, but not sustained hypoxia (SH) of the same duration, was accompanied by several posttranslational modifications of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II, Rpb1, including hydroxylation of proline 1465, phosphorylation of serine 5 residues within the C-terminal domain, and nondegradative ubiquitylation. These modifications were found to occur in two regions of the brain, hippocampal region CA1 and the prefrontal cortex, but not in neocortex, brainstem and CA3 region of hippocampus. We also found that mice exposed to 14 or 30 days of IH, but not SH, demonstrated cognitive deficits in behavioral assays. Furthermore, by using the pheochromocytoma-derived PC12 cell line, we showed that, under in vitro IH conditions, induction of Rpb1 hydroxylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitylation required that the von Hippel-Lindau protein be present. We hypothesize that the observed modifications of Rpb1 participate in regulating the expression of genes involved in mediating cognitive deficits evoked by chronic IH.
Figures






References
-
- Bartlett DJ, Rae C, Thompson CH, Byth K, Joffe DA, Enright, Grunstein RR. Hippocampal area metabolites relate to severity and cognitive function in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. 2004;5:593–596. - PubMed
-
- Bassetti CL, Milanova M, Gugger M. Sleep-disordered breathing and acute ischemic stroke: diagnosis, risk factors, treatment, evolution, and long-term clinical outcome. Stroke. 2006;37:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Beebe DW, Gozal D. Obstructive sleep apnea and the prefrontal cortex: towards a comprehensive model linking nocturnal upper airway obstruction to daytime cognitive and behavioral deficits. J Sleep Res. 2002;11:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Carty SM, Greenleaf AF. Hyperphosphorylated C-terminal repeat domain bv associating proteins in the nuclear proteome link transcription to DNA/chromatin modification and RNA processing. Mol Proteomics. 2002;1:598–610. - PubMed
-
- Czyzyk-Krzeska MF, Furnari BA, Lawson EE, Millhorn DE. Hypoxia increases rate of transcription and stability of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:760–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

