Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load
- PMID: 19095135
- PMCID: PMC2637465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.027
Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load
Abstract
Objectives: This study was designed to investigate: 1) relationships between serum ST2 levels and hemodynamic/neurohormonal variables; 2) myocardial ST2 production; and the 3) expression of ST2, membrane-anchored ST2L, and its ligand, interleukin (IL)-33, in myocardium, endothelium, and leukocytes from patients with left ventricular (LV) pressure overload and congestive cardiomyopathy.
Background: Serum levels of ST2 are elevated in heart failure. The relationship of ST2 to hemodynamic variables, source of ST2, and expression of ST2L and IL-33 in the cardiovascular system are unknown.
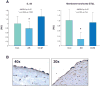
Methods: Serum ST2 (pg/ml; median [25th, 75th percentile]) was measured in patients with LV hypertrophy (aortic stenosis) (n = 45), congestive cardiomyopathy (n = 53), and controls (n = 23). ST2 was correlated to N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, C-reactive protein, and hemodynamic variables. Coronary sinus and arterial blood sampling determined myocardial gradient (production) of ST2. The levels of ST2, ST2L, and IL-33 were measured (reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction) in myocardial biopsies and leukocytes. The ST2 protein production was evaluated in human endothelial cells. The IL-33 protein expression was determined (immunohistochemistry) in coronary artery endothelium.
Results: The ST2 protein was elevated in aortic stenosis (103 [65, 165] pg/ml, p < 0.05) and congestive cardiomyopathy (194 [69, 551] pg/ml, p < 0.01) versus controls (49 [4, 89] pg/ml) and correlated with B-type natriuretic peptide (r = 0.5, p < 0.05), C-reactive protein (r = 0.6, p < 0.01), and LV end-diastolic pressure (r = 0.38, p < 0.03). The LV ST2 messenger ribonucleic acid was similar in aortic stenosis and congestive cardiomyopathy versus control (p = NS). No myocardial ST2 protein gradient was observed. Endothelial cells secreted ST2. The IL-33 protein was expressed in coronary artery endothelium. Leukocyte ST2L and IL-33 levels were highly correlated (r = 0.97, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: In human hypertrophy and failure, serum ST2 correlates with the diastolic load. Though the heart, endothelium, and leukocytes express components of ST2/ST2L/IL-33 pathway, the source of circulating serum ST2 is extra-myocardial.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state no conflicts of interest
Figures

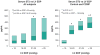




References
-
- Januzzi JL, Jr, Peacock WF, Maisel AS, et al. Measurement of the interleukin family member ST2 in patients with acute dyspnea: results from the PRIDE (Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:607–13. - PubMed
-
- Shimpo M, Morrow DA, Weinberg EO, et al. Serum levels of the interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2 predict mortality and clinical outcome in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109:2186–90. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg EO, Shimpo M, Hurwitz S, Tominaga S, Rouleau JL, Lee RT. Identification of serum soluble ST2 receptor as a novel heart failure biomarker. Circulation. 2003;107:721–6. - PubMed
-
- Mueller T, Dieplinger B, Gegenhuber A, Poelz W, Pacher R, Haltmayer M. Increased plasma concentrations of soluble ST2 are predictive for 1-year mortality in patients with acute destabilized heart failure. Clin Chem. 2008;54:752–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

