Direct profiling of tissue lipids by MALDI-TOFMS
- PMID: 19095508
- PMCID: PMC2945280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.11.033
Direct profiling of tissue lipids by MALDI-TOFMS
Abstract
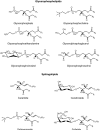
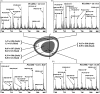
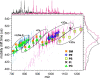
Advances in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOFMS) have allowed for the direct analysis of biological molecules from tissue. Although most of the early studies of direct tissue profiling by MALDI-TOFMS have focused on proteins and peptides, analysis of lipids has increased dramatically in recent years. This review gives an overview of the factors to consider when analyzing lipids directly from tissue and some recent examples of the use of MALDI-TOFMS for the direct profiling of lipids in tissue.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

