In vivo commitment and functional tissue regeneration using human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal cells
- PMID: 19095799
- PMCID: PMC2634917
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809680106
In vivo commitment and functional tissue regeneration using human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal cells
Abstract
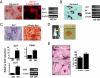
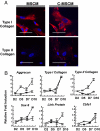
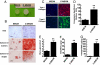
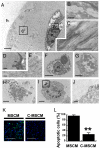
Development of clinically relevant regenerative medicine therapies using human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) requires production of a simple and readily expandable cell population that can be directed to form functional 3D tissue in an in vivo environment. We describe an efficient derivation method and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from hESCs (hESCd-MSCs) that have multilineage differentiation potential and are capable of producing fat, cartilage, and bone in vitro. Furthermore, we highlight their in vivo survival and commitment to the chondrogenic lineage in a microenvironment comprising chondrocyte-secreted morphogenetic factors and hydrogels. Normal cartilage architecture was established in rat osteochondral defects after treatment with chondrogenically-committed hESCd-MSCs. In view of the limited available cell sources for tissue engineering applications, these embryonic-derived cells show significant potential in musculoskeletal tissue regeneration applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lerou PH, Daley GQ. Therapeutic potential of embryonic stem cells. Blood Rev. 2005;19:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

