p47phox deficiency induces macrophage dysfunction resulting in progressive crystalline macrophage pneumonia
- PMID: 19095958
- PMCID: PMC2631328
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080555
p47phox deficiency induces macrophage dysfunction resulting in progressive crystalline macrophage pneumonia
Abstract
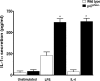
Nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-deficient (p47(phox-/-)) mice are a model of human chronic granulomatous disease; these mice are prone to develop systemic infections and inflammatory diseases. The use of antibiotic (Bactrim) prophylaxis in a specific pathogen-free environment, however, impedes infection in the majority of p47(phox-/-) mice. We examined infection-free p47(phox-/-) mice between 1 and 14 months of age and found that they developed proliferative macrophage lesions containing Ym1/Ym2 protein and crystals in lung, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. Here, we show that the lung lesions progressed from single macrophages with intracellular Ym1/Ym2 protein crystals to severe diffuse crystalline macrophage pneumonia without histological evidence of either granulation tissue or pulmonary fibrosis. Ym1/Ym2 is a chitinase-like secretory protein that is transiently induced in alternatively activated macrophages during T-helper (Th)2-biased pathogenesis and during chemical and traumatic inflammation. Bronchoalveolar lavage from p47(phox-/-) mice contained significantly higher levels of Th-1 (interferon-gamma), Th-2 (interleukin-4), and Th-17 (interleukin-17)-associated cytokines than wild-type mice, as well as copious amounts of interleukin-12, indicating that Ym1-secreting p47(phox-/-) macrophages are also integrated into classically activated macrophage responses. These results suggest that p47(phox-/-) macrophages are extremely pliable, due in part to an intrinsic dysfunction of macrophage activation pathways that allows for distinct classical or alternative activation phenotypes.
Figures





References
-
- Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol. 2000;164:6166–6173. - PubMed
-
- Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CF, Mosser DM. A novel phenotype for an activated macrophage: the type 2 activated macrophage. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72:101–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

