Muscleblind-like proteins: similarities and differences in normal and myotonic dystrophy muscle
- PMID: 19095965
- PMCID: PMC2631334
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080520
Muscleblind-like proteins: similarities and differences in normal and myotonic dystrophy muscle
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2009 Mar;174(3):1120-1
Abstract
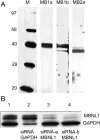
In myotonic dystrophy, muscleblind-like protein 1 (MBNL1) protein binds specifically to expanded CUG or CCUG repeats, which accumulate as discrete nuclear foci, and this is thought to prevent its function in the regulation of alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs. There is strong evidence for the role of the MBNL1 gene in disease pathology, but the roles of two related genes, MBNL2 and MBNL3, are less clear. Using new monoclonal antibodies specific for each of the three gene products, we found that MBNL2 decreased during human fetal development and myoblast culture, while MBNL1 was unchanged. In Duchenne muscular dystrophy muscle, MBNL2 was elevated in immature, regenerating fibres compared with mature fibres, supporting some developmental role for MBNL2. MBNL3 was found only in C2C12 mouse myoblasts. Both MBNL1 and MBNL2 were partially sequestered by nuclear foci of expanded repeats in adult muscle and cultured cells from myotonic dystrophy patients. In adult muscle nucleoplasm, both proteins were reduced in myotonic dystrophy type 1 compared with an age-matched control. In normal human myoblast cultures, MBNL1 and MBNL2 always co-distributed but their distribution could change rapidly from nucleoplasmic to cytoplasmic. Functional differences between MBNL1 and MBNL2 have not yet been found and may prove quite subtle. The dominance of MBNL1 in mature, striated muscle would explain why ablation of the mouse mbnl1 gene alone is sufficient to cause a myotonic dystrophy.
Figures








References
-
- Harper PS. London: WB Saunders; Myotonic Dystrophy. (ed 3) 2004
-
- Day JW, Ranum LP. RNA pathogenesis of the myotonic dystrophies. Neuromuscul Disord. 2005;15:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Machuca-Tzili L, Brook D, Hilton-Jones D. Clinical and molecular aspects of the myotonic dystrophies: a review. Muscle Nerve. 2005;32:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Brook JD, McCurrach ME, Harley HG, Buckler AJ, Church D, Aburatani H, Hunter K, Stanton VP, Thirion JP, Hudson T, Sohn R, Zemelman B, Snell RG, Rundle SA, Crow S, Davies J, Shelbourne P, Buxton J, Jones C, Juvonen V, Johnson K, Harper PS, Shaw DJ, Housman DE. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992;68:799–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

