Identification of glucose-regulated miRNAs from pancreatic {beta} cells reveals a role for miR-30d in insulin transcription
- PMID: 19096044
- PMCID: PMC2648717
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1211209
Identification of glucose-regulated miRNAs from pancreatic {beta} cells reveals a role for miR-30d in insulin transcription
Abstract
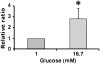
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding ribonucleotides that bind mRNAs and function mainly as translational repressors in mammals. MicroRNAs have been implicated to play a role in many diseases, including diabetes. Several reports indicate an important function for miRNAs in insulin production as well as insulin secretion. We have recently carried out a screen in the pancreatic beta-cell line MIN6 to identify miRNAs with altered abundance in response to changes in glucose concentrations. This screen resulted in identification of 61 glucose-regulated miRNAs from a total of 108 miRNAs detectable in MIN6 cells. Many of the identified miRNAs, including miR-124a, miR-107, and miR-30d were up-regulated in the presence of high glucose. Only a few of the miRNAs, including miR-296, miR-484, and miR-690 were significantly down-regulated by high glucose treatment. Interestingly, we found that overexpression of miR-30d, one of the miRNAs up-regulated by glucose, increased insulin gene expression, while inhibition of miR-30d abolished glucose-stimulated insulin gene transcription. Overexpression or inhibition of miR-30d did not have any effect on insulin secretion. These data suggest that the putative target genes of miR-30d may be negative regulators of insulin gene expression.
Figures




References
-
- Baroukh N., Ravier M.A., Loder M.K., Hill E.V., Bounacer A., Scharfmann R., Rutter G.A., Van Obberghen E. MicroRNA-124a regulates Foxa2 expression and intracellular signaling in pancreatic β-cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:19575–19588. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Cuellar T.L., McManus M.T. MicroRNAs and endocrine biology. J. Endocrinol. 2005;187:327–332. - PubMed
-
- de Hoon M.J., Imoto S., Nolan J., Miyano S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1453–1454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
