Adaptive-optics optical coherence tomography for high-resolution and high-speed 3D retinal in vivo imaging
- PMID: 19096728
- PMCID: PMC2605068
- DOI: 10.1364/opex.13.008532
Adaptive-optics optical coherence tomography for high-resolution and high-speed 3D retinal in vivo imaging
Abstract
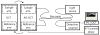
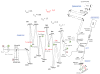
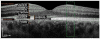
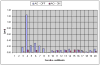
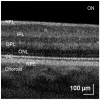
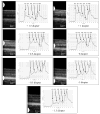
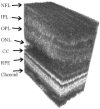
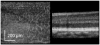
We have combined Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography (FD-OCT) with a closed-loop adaptive optics (AO) system using a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor and a bimorph deformable mirror. The adaptive optics system measures and corrects the wavefront aberration of the human eye for improved lateral resolution (~4 μm) of retinal images, while maintaining the high axial resolution (~6 μm) of stand alone OCT. The AO-OCT instrument enables the three-dimensional (3D) visualization of different retinal structures in vivo with high 3D resolution (4×4×6 μm). Using this system, we have demonstrated the ability to image microscopic blood vessels and the cone photoreceptor mosaic.
Figures



References
-
- Fercher AF, Hitzenberger CK, Kamp G, Elzaiat Y. Measurement of intraocular distances by backscattering spectral interferometry. Opt Commun. 1995;117:43–48.
-
- Wojtkowski M, Leitgeb R, Kowalczyk A, Bajraszewski T, Fercher AF. In Vivo human retinal imaging by fourier domain optical coherence tomography. J Biomed Opt. 2002;7:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Nassif NA, Cense B, Park BH, Pierce MC, Yun SH, Bouma BE, Tearney GJ, Chen TC, de Boer JF. In vivo high-resolution video-rate spectral-domain optical coherence tomography of the human retina and optic nerve. Opt Express. 2004. pp. 367–376. http://www.opticsexpress.org/abstract.cfm?URI=OPEX-12-3-367. - PubMed
-
- de Boer JF, Cense B, Park BH, Pierce MC, Tearney GJ, Bouma BE. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2003;28:2067–2069. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

