Aquaporin-1 gene transfer to correct radiation-induced salivary hypofunction
- PMID: 19096789
- PMCID: PMC2760475
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_20
Aquaporin-1 gene transfer to correct radiation-induced salivary hypofunction
Abstract
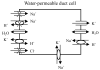
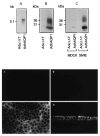
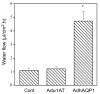
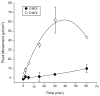
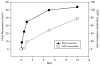
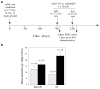
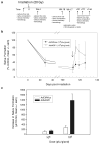
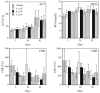
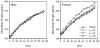
Irradiation damage to salivary glands is a common iatrogenic consequence of treatment for head and neck cancers. The subsequent lack of saliva production leads to many functional and quality-of-life problems for affected patients and there is no effective conventional therapy. To address this problem, we developed an in vivo gene therapy strategy involving viral vector-mediated transfer of the aquaporin-1 cDNA to irradiation-damaged glands and successfully tested it in two pre-clinical models (irradiated rats and miniature pigs), as well as demonstrated its safety in a large toxicology and biodistribution study. Thereafter, a clinical research protocol was developed that has received approval from all required authorities in the United States. Patients are currently being enrolled in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Adesanya MR, Redman RS, Baum BJ, et al. Immediate inflammatory responses to adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in rat salivary glands. Hum Gene Ther. 1996;7:1085–1093. - PubMed
-
- Baum BJ. Principles of saliva secretion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;694:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Baum BJ, Wang S, Cukierman E, et al. Re-engineering the functions of a terminally differentiated epithelial cell in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;875:294–300. - PubMed
-
- Baum BJ, Wellner RB, Zheng C. Gene transfer to salivary glands. Int Rev Cytol. 2002;213:93–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

