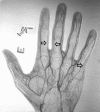
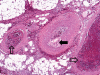
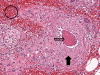
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome triggered by sepsis
- PMID: 19096893
- PMCID: PMC2642545
- DOI: 10.1007/s11420-008-9103-6
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome triggered by sepsis
Figures



References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1191/0961203303lu394oa', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203303lu394oa'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12892393', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12892393/'}]}
- Asherson RA, Cervera R, de Groot PG et al (2003) Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Registry Project Group. Catastrosphic antiphospholipid syndrome: international consensus statement on classification criteria and treatment guidelines. Lupus 12:530–534 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1161/hh0102.102795', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1161/hh0102.102795'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11786515', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11786515/'}]}
- Rand JH (2002) Molecular pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome. Circ Res 90:29–37 - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Asherson RA (2006) Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. J Pathophy Haem Thrombosis 181–186 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/rheumatology/41.8.924', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/41.8.924'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12154210', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12154210/'}]}
- Erkan D, Yazici Y, Peterson MG et al (2002) A cross-sectional study of clinical thrombotic risk factors and preventive treatments in antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 41:924–929 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1177/0885066606287041', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066606287041'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16672637', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16672637/'}]}
- Vero SK, Asherson RA, Erkan D (2006) Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. J Intensive Care Med 21:144–159 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

