Retrospective 3D registration of trabecular bone MR images for longitudinal studies
- PMID: 19097098
- PMCID: PMC2731663
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21551
Retrospective 3D registration of trabecular bone MR images for longitudinal studies
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate an automatic 3D registration algorithm for serial high-resolution images of trabecular bone (TB) in studies designed to evaluate the response of the trabecular architecture to intervention or disease progression.
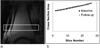
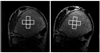
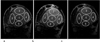
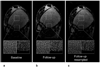
Materials and methods: An efficient algorithm for registering high-resolution 3D images of TB is presented. The procedure identifies the six parameters of rigid displacement between two scans performed at different timepoints. By assuming a relatively small through-plane rotation, considerable time is saved by combining the results of a collection of regional 2D registrations throughout the TB region of interest (ROI). The algorithm was applied to 26 pairs of MR images acquired 6 months apart. Reproducibility of local TB structural parameters (plate, rod, and junction density) computed in manually selected regions were compared between baseline and registered follow-up images.
Results: All 26 registrations were completed successfully in less than 30 seconds per image pair. The resampled follow-up images agreed with baseline to around one pixel throughout the volume at 137 x 137 x 410 microm(3) image resolution. Structural parameters in each region correlated well from baseline to follow-up with intraclass correlation coefficients ranging between 85%-97% for TB plate density. Interregional variations in the parameters were large as compared with intraregion reproducibility.
Conclusion: The proposed algorithm was successful in automatically registering baseline and follow-up TB images in a translational study, and may be useful in regional analyses in longitudinal MR studies of TB architecture.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional image registration of MR proximal femur images for the analysis of trabecular bone parameters.Med Phys. 2008 Oct;35(10):4630-9. doi: 10.1118/1.2977764. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18975709 Free PMC article.
-
CLASSIC: consistent longitudinal alignment and segmentation for serial image computing.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2005;19:101-13. doi: 10.1007/11505730_9. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2005. PMID: 17354688
-
3-D/2-D registration by integrating 2-D information in 3-D.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006 Jan;25(1):17-27. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2005.859715. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2006. PMID: 16398411
-
A novel local thresholding algorithm for trabecular bone volume fraction mapping in the limited spatial resolution regime of in vivo MRI.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005 Dec;24(12):1574-85. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2005.859192. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005. PMID: 16353372 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of 3D/2D registration methods for image-guided interventions.Med Image Anal. 2012 Apr;16(3):642-61. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Med Image Anal. 2012. PMID: 20452269 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of μMRI-Based virtual bone biopsy for structural and mechanical analysis at the distal tibia at 7T field strength.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011 Feb;33(2):372-81. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22439. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21274979 Free PMC article.
-
Precision of volumetric assessment of proximal femur microarchitecture from high-resolution 3T MRI.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2015 Jan;10(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s11548-014-1009-9. Epub 2014 May 6. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2015. PMID: 24799271 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanical parameters of trabecular bone estimated from in vivo high-resolution magnetic resonance images at 3 tesla field strength.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 May;31(5):1157-68. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22158. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20432352 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Low-intensity Vibration to Improve Bone Health in Patients with End-stage Renal Disease Is Highly Dependent on Compliance and Muscle Response.Acad Radiol. 2017 Nov;24(11):1332-1342. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.05.014. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Acad Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28652048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Computationally-optimized bone mechanical modeling from high-resolution structural images.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035525. Epub 2012 Apr 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heaney RP. Is there a role for bone quality in fragility fractures? Calcified Tissue International. 1993;53(S1):S3–S6. - PubMed
-
- Kleerekoper M, Villanueva AR, Stanciu J, Sudhaker Rao D, Parfitt AM. The Role of Three-Dimensional Trabecular Microstructure in the Pathogenesis of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Calcified Tissue International. 1985;37:594–597. - PubMed
-
- Aaron JE, Shore PA, Shore RC, Beneton M, Kanis JA. Trabecular architecture in women and men of similar bone mass with and without vertebral fracture: II. Three-dimensional histology. Bone. 2000;27(2):277–282. - PubMed
-
- Recker RR. Architecture and vertebral fracture. Calcified Tissue International. 1993;53(Suppl 1):S139–S142. - PubMed
-
- Legrand E, Chappard D, Pascaretti C, et al. Trabecular bone microarchitecture, bone mineral density and vertebral fractures in male osteoporosis. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2000;15:13–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

